Page 239 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 239
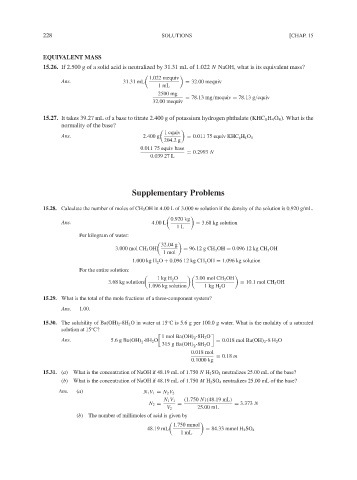
228 SOLUTIONS [CHAP. 15
EQUIVALENT MASS
15.26. If 2.500 g of a solid acid is neutralized by 31.31 mL of 1.022 N NaOH, what is its equivalent mass?
1.022 mequiv
Ans. 31.31 mL = 32.00 mequiv
1mL
2500 mg
= 78.13 mg/mequiv = 78.13 g/equiv
32.00 mequiv
15.27. It takes 39.27 mL of a base to titrate 2.400 g of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC 8 H 4 O 4 ). What is the
normality of the base?
1 equiv
Ans. 2.400 g = 0.011 75 equiv KHC H 4 O 4
8
204.2g
0.011 75 equiv base
= 0.2993 N
0.039 27 L
Supplementary Problems
15.28. Calculate the number of moles of CH 3 OH in 4.00 L of 3.000 m solution if the density of the solution is 0.920 g/mL.
0.920 kg
Ans. 4.00 L = 3.68 kg solution
1L
Per kilogram of water:
32.04 g
3.000 mol CH 3 OH = 96.12gCH OH = 0.096 12 kg CH OH
3
3
1 mol
1.000 kg H O + 0.096 12 kg CH OH = 1.096 kg solution
2
3
For the entire solution:
1kgH O 3.00 mol CH 3 OH
3.68 kg solution 2 = 10.1 mol CH 3 OH
1.096 kg solution 1kgH O
2
15.29. What is the total of the mole fractions of a three-component system?
Ans. 1.00.
15.30. The solubility of Ba(OH) 2 ·8H 2 O in water at 15 C is 5.6 g per 100.0 g water. What is the molality of a saturated
◦
◦
solution at 15 C?
1 mol Ba(OH) 2 ·8H 2 O
Ans. 5.6gBa(OH) ·8H 2 O = 0.018 mol Ba(OH) 2 ·8H 2 O
2
315gBa(OH) ·8H 2 O
2
0.018 mol
= 0.18 m
0.1000 kg
15.31. (a) What is the concentration of NaOH if 48.19 mL of 1.750 N H 2 SO 4 neutralizes 25.00 mL of the base?
(b) What is the concentration of NaOH if 48.19 mL of 1.750 M H 2 SO 4 neutralizes 25.00 mL of the base?
Ans. (a) N 1 V 1 = N 2 V 2
(1.750 N)(48.19 mL)
N 1 V 1
N 2 = = = 3.373 N
V 2 25.00 mL
(b) The number of millimoles of acid is given by
1.750 mmol
48.19 mL = 84.33 mmol H 2 SO 4
1mL