Page 30 - Sedimentology and Stratigraphy
P. 30
Final Proof page 17
Final
Final
page
Proof
Proof
02
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy
and
02
9781405193795_4_0
9781405193795_4_0
page
Name:
Compositor
Compositor
ARaju
ARaju
Name:
8:14pm
26.2.2009 8:14pm Compositor Name: ARaju
17
17
8:14pm
26.2.2009
26.2.2009
Nichols/Sedimentology and Stratigraphy 9781405193795_4_002
Nichols/Sedimentology
and
Nichols/Sedimentology
Sand and Sandstone 17
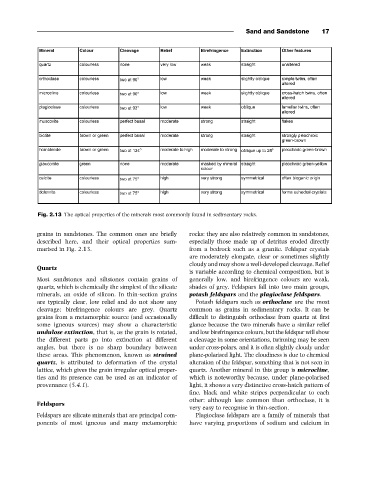
Fig. 2.13 The optical properties of the minerals most commonly found in sedimentary rocks.
grains in sandstones. The common ones are briefly rocks: they are also relatively common in sandstones,
described here, and their optical properties sum- especially those made up of detritus eroded directly
marised in Fig. 2.13. from a bedrock such as a granite. Feldspar crystals
are moderately elongate, clear or sometimes slightly
cloudy and may show a well-developed cleavage. Relief
Quartz
is variable according to chemical composition, but is
Most sandstones and siltstones contain grains of generally low, and birefringence colours are weak,
quartz, which is chemically the simplest of the silicate shades of grey. Feldspars fall into two main groups,
minerals, an oxide of silicon. In thin-section grains potash feldspars and the plagioclase feldspars.
are typically clear, low relief and do not show any Potash feldspars such as orthoclase are the most
cleavage; birefringence colours are grey. Quartz common as grains in sedimentary rocks. It can be
grains from a metamorphic source (and occasionally difficult to distinguish orthoclase from quartz at first
some igneous sources) may show a characteristic glance because the two minerals have a similar relief
undulose extinction, that is, as the grain is rotated, and low birefringence colours, but the feldspar will show
the different parts go into extinction at different a cleavage in some orientations, twinning may be seen
angles, but there is no sharp boundary between under cross-polars, and it is often slightly cloudy under
these areas. This phenomenon, known as strained plane-polarised light. The cloudiness is due to chemical
quartz, is attributed to deformation of the crystal alteration of the feldspar, something that is not seen in
lattice, which gives the grain irregular optical proper- quartz. Another mineral in this group is microcline,
ties and its presence can be used as an indicator of which is noteworthy because, under plane-polarised
provenance (5.4.1). light, it shows a very distinctive cross-hatch pattern of
fine, black and white stripes perpendicular to each
other: although less common than orthoclase, it is
Feldspars
very easy to recognise in thin-section.
Feldspars are silicate minerals that are principal com- Plagioclase feldspars are a family of minerals that
ponents of most igneous and many metamorphic have varying proportions of sodium and calcium in