Page 162 - Sensing, Intelligence, Motion : How Robots and Humans Move in an Unstructured World
P. 162
EXERCISES 137
L
L 5 2
L 4
L 1
T H 1
L 3
H 3
S
H o
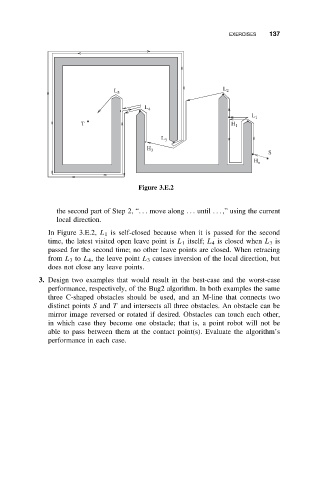
Figure 3.E.2
the second part of Step 2, “... move along .. . until ... ,” using the current
local direction.
In Figure 3.E.2, L 1 is self-closed because when it is passed for the second
time, the latest visited open leave point is L 1 itself; L 4 is closed when L 3 is
passed for the second time; no other leave points are closed. When retracing
from L 3 to L 4 , the leave point L 3 causes inversion of the local direction, but
does not close any leave points.
3. Design two examples that would result in the best-case and the worst-case
performance, respectively, of the Bug2 algorithm. In both examples the same
three C-shaped obstacles should be used, and an M-line that connects two
distinct points S and T and intersects all three obstacles. An obstacle can be
mirror image reversed or rotated if desired. Obstacles can touch each other,
in which case they become one obstacle; that is, a point robot will not be
able to pass between them at the contact point(s). Evaluate the algorithm’s
performance in each case.