Page 297 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 297
The Role of Sensors and Contr ol Technology in CIM
step. The objectives and decision variables, as related to elements or 255
units for all possible levels, are outlined in the following sections.
5.6.1 Structured Analysis and Design Technique (SADT)
The structured analysis and design technique is a structured method-
ology. It combines the graphical diagramming language of structured
analysis (SA) with the formal thought discipline of a design technique
(DT). The advantage of SADT is that it contains a formalized notation
and procedure for defining system functions.
Psychological studies have shown that the human mind has diffi-
culty grasping more than five to seven concepts at one time. Based on
this observation, SADT follows the structured analysis maxim: “Every-
thing worth saying must be expressed in six or fewer pieces.” Limiting
each part to six elements ensures that individual parts are not too dif-
ficult to understand. Even complex manufacturing systems can be sub-
jected to top-down decomposition without becoming overwhelming.
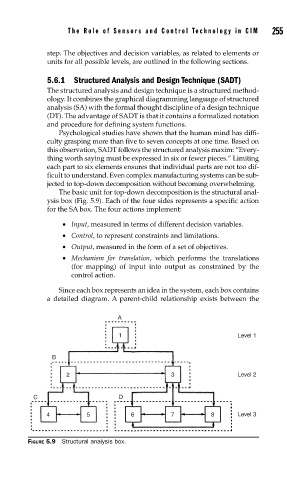
The basic unit for top-down decomposition is the structural anal-
ysis box (Fig. 5.9). Each of the four sides represents a specific action
for the SA box. The four actions implement:
• Input, measured in terms of different decision variables.
• Control, to represent constraints and limitations.
• Output, measured in the form of a set of objectives.
• Mechanism for translation, which performs the translations
(for mapping) of input into output as constrained by the
control action.
Since each box represents an idea in the system, each box contains
a detailed diagram. A parent-child relationship exists between the
A
1 Level 1
B
2 3 Level 2
C D
4 5 6 7 8 Level 3
FIGURE 5.9 Structural analysis box.