Page 64 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 64
26
Cha p te r
O n e
• The epoxy resin enclosure has three functions. It is designed
to allow the most light to escape from the semiconductor, it
focuses the light and protects the LED semiconductor from
the elements.
• The entire LED unit is totally embedded in an epoxy. This is
what make LEDs virtually indestructible. There are no loose
or moving parts within the solid epoxy enclosure.
Thus, a light-emitting diode (LED) is essentially a PN junction
semiconductor diode that emits light when current is applied. It is a
solid-state device that controls current without heated filaments and
is therefore highly reliable. LED performance is based on a few pri-
mary characteristics:
1.13.1 Monochromatic LEDs
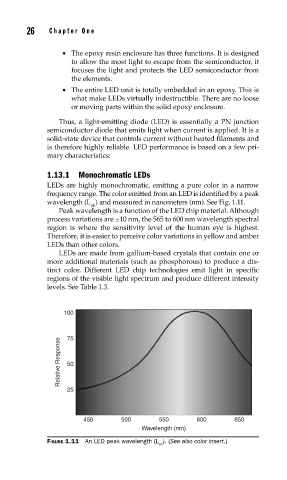
LEDs are highly monochromatic, emitting a pure color in a narrow
frequency range. The color emitted from an LED is identified by a peak
wavelength (L ) and measured in nanometers (nm). See Fig. 1.11.
pk
Peak wavelength is a function of the LED chip material. Although
process variations are ±10 nm, the 565 to 600 nm wavelength spectral
region is where the sensitivity level of the human eye is highest.
Therefore, it is easier to perceive color variations in yellow and amber
LEDs than other colors.
LEDs are made from gallium-based crystals that contain one or
more additional materials (such as phosphorous) to produce a dis-
tinct color. Different LED chip technologies emit light in specific
regions of the visible light spectrum and produce different intensity
levels. See Table 1.3.
100
Relative Response 75
50
25
450 500 550 600 650
Wavelength (nm)
FIGURE 1.11 An LED peak wavelength (L ). (See also color insert.)
pk