Page 86 - Separation process engineering
P. 86
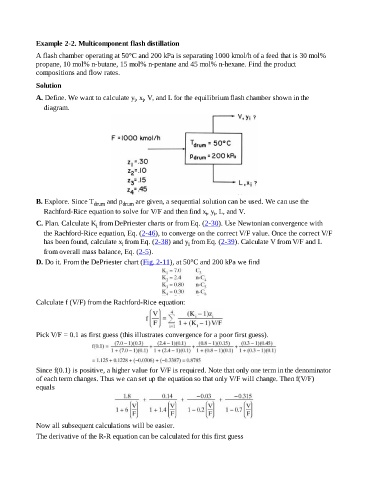
Example 2-2. Multicomponent flash distillation
A flash chamber operating at 50°C and 200 kPa is separating 1000 kmol/h of a feed that is 30 mol%
propane, 10 mol% n-butane, 15 mol% n-pentane and 45 mol% n-hexane. Find the product
compositions and flow rates.
Solution
A. Define. We want to calculate y, x, V, and L for the equilibrium flash chamber shown in the
i
i
diagram.
B. Explore. Since T and p are given, a sequential solution can be used. We can use the
drum drum
Rachford-Rice equation to solve for V/F and then find x, y, L, and V.
i
i
C. Plan. Calculate K from DePriester charts or from Eq. (2-30). Use Newtonian convergence with
i
the Rachford-Rice equation, Eq. (2-46), to converge on the correct V/F value. Once the correct V/F
has been found, calculate x from Eq. (2-38) and y from Eq. (2-39). Calculate V from V/F and L
i
i
from overall mass balance, Eq. (2-5).
D. Do it. From the DePriester chart (Fig. 2-11), at 50°C and 200 kPa we find
Calculate f (V/F) from the Rachford-Rice equation:
Pick V/F = 0.1 as first guess (this illustrates convergence for a poor first guess).
Since f(0.1) is positive, a higher value for V/F is required. Note that only one term in the denominator
of each term changes. Thus we can set up the equation so that only V/F will change. Then f(V/F)
equals
Now all subsequent calculations will be easier.
The derivative of the R-R equation can be calculated for this first guess