Page 45 - Silence in Intercultural Communication
P. 45
32 Silence in Intercultural Communication
Socio-psychological Linguistic domain
domain
Preferred politeness strategies
Preferred mode
of communication
Preferred
Patterns of
Degree of participant participant
structure
threat to structure
face
Language anxiety
Participants’
Lexico- orientation
grammatical to turn-taking
Shared Personality competence Norms of
orientation Perceptions turn-taking
to face and
politeness of self and Level of Fluency
other commitment
participants Significance
Language of
Preferred learning processing time non-verbal
style and topic behaviour Norms of
Knowledge non-verbal
schema behaviour
and its
Reaction speed inter-
pretation
Participants’
knowledge
Topic schema
Norms
of Shared
relevance Participants’ speed knowledge
of reaction
Norms of reaction speed
Cognitive Domain
Individual level
Situational level
Sociocultural level
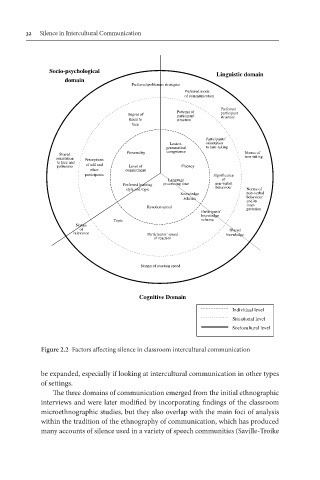
Figure 2.2 Factors affecting silence in classroom intercultural communication
be expanded, especially if looking at intercultural communication in other types
of settings.
The three domains of communication emerged from the initial ethnographic
interviews and were later modified by incorporating findings of the classroom
microethnographic studies, but they also overlap with the main foci of analysis
within the tradition of the ethnography of communication, which has produced
many accounts of silence used in a variety of speech communities (Saville-Troike