Page 105 -
P. 105
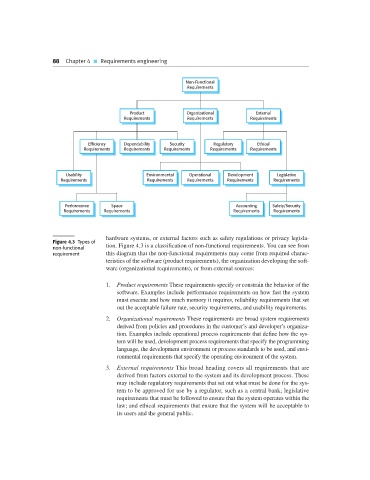
88 Chapter 4 Requirements engineering
Non-Functional
Requirements
Product Organizational External
Requirements Requirements Requirements
Efficiency Dependability Security Regulatory Ethical
Requirements Requirements Requirements Requirements Requirements
Usability Environmental Operational Development Legislative
Requirements Requirements Requirements Requirements Requirements
Performance Space Accounting Safety/Security
Requirements Requirements Requirements Requirements
hardware systems, or external factors such as safety regulations or privacy legisla-
Figure 4.3 Types of
non-functional tion. Figure 4.3 is a classification of non-functional requirements. You can see from
requirement this diagram that the non-functional requirements may come from required charac-
teristics of the software (product requirements), the organization developing the soft-
ware (organizational requirements), or from external sources:
1. Product requirements These requirements specify or constrain the behavior of the
software. Examples include performance requirements on how fast the system
must execute and how much memory it requires, reliability requirements that set
out the acceptable failure rate, security requirements, and usability requirements.
2. Organizational requirements These requirements are broad system requirements
derived from policies and procedures in the customer’s and developer’s organiza-
tion. Examples include operational process requirements that define how the sys-
tem will be used, development process requirements that specify the programming
language, the development environment or process standards to be used, and envi-
ronmental requirements that specify the operating environment of the system.
3. External requirements This broad heading covers all requirements that are
derived from factors external to the system and its development process. These
may include regulatory requirements that set out what must be done for the sys-
tem to be approved for use by a regulator, such as a central bank; legislative
requirements that must be followed to ensure that the system operates within the
law; and ethical requirements that ensure that the system will be acceptable to
its users and the general public.