Page 227 -
P. 227
210 Chapter 8 Software testing
Test Test Test Test
Cases Data Results Reports
Design Test Prepare Test Run Program Compare Results
Cases Data with Test Data to Test Cases
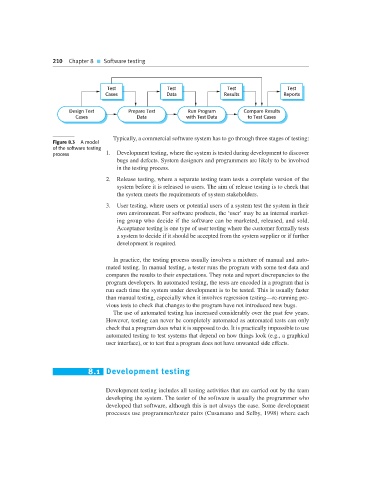
Typically, a commercial software system has to go through three stages of testing:
Figure 8.3 A model
of the software testing
process 1. Development testing, where the system is tested during development to discover
bugs and defects. System designers and programmers are likely to be involved
in the testing process.
2. Release testing, where a separate testing team tests a complete version of the
system before it is released to users. The aim of release testing is to check that
the system meets the requirements of system stakeholders.
3. User testing, where users or potential users of a system test the system in their
own environment. For software products, the ‘user’ may be an internal market-
ing group who decide if the software can be marketed, released, and sold.
Acceptance testing is one type of user testing where the customer formally tests
a system to decide if it should be accepted from the system supplier or if further
development is required.
In practice, the testing process usually involves a mixture of manual and auto-
mated testing. In manual testing, a tester runs the program with some test data and
compares the results to their expectations. They note and report discrepancies to the
program developers. In automated testing, the tests are encoded in a program that is
run each time the system under development is to be tested. This is usually faster
than manual testing, especially when it involves regression testing—re-running pre-
vious tests to check that changes to the program have not introduced new bugs.
The use of automated testing has increased considerably over the past few years.
However, testing can never be completely automated as automated tests can only
check that a program does what it is supposed to do. It is practically impossible to use
automated testing to test systems that depend on how things look (e.g., a graphical
user interface), or to test that a program does not have unwanted side effects.
8.1 Development testing
Development testing includes all testing activities that are carried out by the team
developing the system. The tester of the software is usually the programmer who
developed that software, although this is not always the case. Some development
processes use programmer/tester pairs (Cusamano and Selby, 1998) where each