Page 55 -
P. 55
38 Chapter 2 Software processes
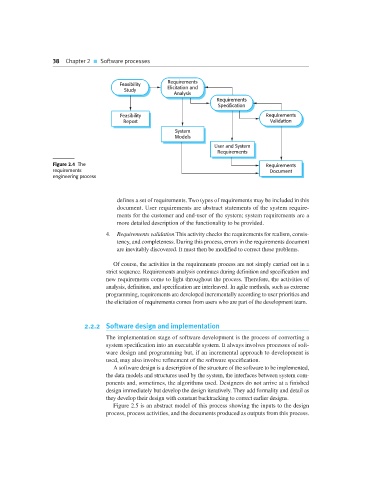
Requirements
Feasibility
Study Elicitation and
Analysis
Requirements
Specification
Feasibility Requirements
Report Validation
System
Models
User and System
Requirements
Figure 2.4 The Requirements
requirements Document
engineering process
defines a set of requirements. Two types of requirements may be included in this
document. User requirements are abstract statements of the system require-
ments for the customer and end-user of the system; system requirements are a
more detailed description of the functionality to be provided.
4. Requirements validation This activity checks the requirements for realism, consis-
tency, and completeness. During this process, errors in the requirements document
are inevitably discovered. It must then be modified to correct these problems.
Of course, the activities in the requirements process are not simply carried out in a
strict sequence. Requirements analysis continues during definition and specification and
new requirements come to light throughout the process. Therefore, the activities of
analysis, definition, and specification are interleaved. In agile methods, such as extreme
programming, requirements are developed incrementally according to user priorities and
the elicitation of requirements comes from users who are part of the development team.
2.2.2 Software design and implementation
The implementation stage of software development is the process of converting a
system specification into an executable system. It always involves processes of soft-
ware design and programming but, if an incremental approach to development is
used, may also involve refinement of the software specification.
A software design is a description of the structure of the software to be implemented,
the data models and structures used by the system, the interfaces between system com-
ponents and, sometimes, the algorithms used. Designers do not arrive at a finished
design immediately but develop the design iteratively. They add formality and detail as
they develop their design with constant backtracking to correct earlier designs.
Figure 2.5 is an abstract model of this process showing the inputs to the design
process, process activities, and the documents produced as outputs from this process.