Page 69 -
P. 69
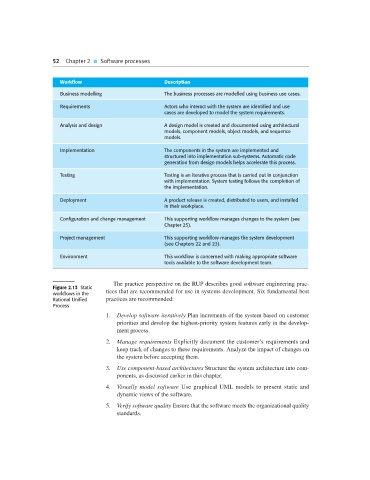
52 Chapter 2 Software processes
Workflow Description
Business modelling The business processes are modelled using business use cases.
Requirements Actors who interact with the system are identified and use
cases are developed to model the system requirements.
Analysis and design A design model is created and documented using architectural
models, component models, object models, and sequence
models.
Implementation The components in the system are implemented and
structured into implementation sub-systems. Automatic code
generation from design models helps accelerate this process.
Testing Testing is an iterative process that is carried out in conjunction
with implementation. System testing follows the completion of
the implementation.
Deployment A product release is created, distributed to users, and installed
in their workplace.
Configuration and change management This supporting workflow manages changes to the system (see
Chapter 25).
Project management This supporting workflow manages the system development
(see Chapters 22 and 23).
Environment This workflow is concerned with making appropriate software
tools available to the software development team.
The practice perspective on the RUP describes good software engineering prac-
Figure 2.13 Static
workflows in the tices that are recommended for use in systems development. Six fundamental best
Rational Unified practices are recommended:
Process
1. Develop software iteratively Plan increments of the system based on customer
priorities and develop the highest-priority system features early in the develop-
ment process.
2. Manage requirements Explicitly document the customer’s requirements and
keep track of changes to these requirements. Analyze the impact of changes on
the system before accepting them.
3. Use component-based architectures Structure the system architecture into com-
ponents, as discussed earlier in this chapter.
4. Visually model software Use graphical UML models to present static and
dynamic views of the software.
5. Verify software quality Ensure that the software meets the organizational quality
standards.