Page 83 -
P. 83
66 Chapter 3 Agile software development
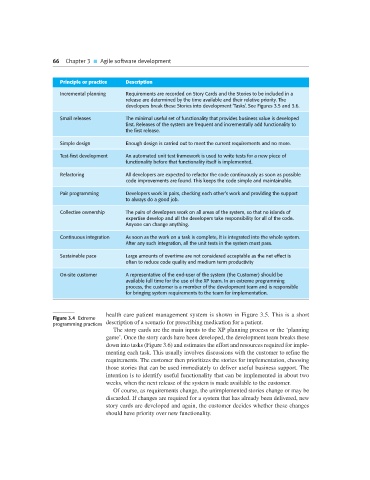
Principle or practice Description
Incremental planning Requirements are recorded on Story Cards and the Stories to be included in a
release are determined by the time available and their relative priority. The
developers break these Stories into development ‘Tasks’. See Figures 3.5 and 3.6.
Small releases The minimal useful set of functionality that provides business value is developed
first. Releases of the system are frequent and incrementally add functionality to
the first release.
Simple design Enough design is carried out to meet the current requirements and no more.
Test-first development An automated unit test framework is used to write tests for a new piece of
functionality before that functionality itself is implemented.
Refactoring All developers are expected to refactor the code continuously as soon as possible
code improvements are found. This keeps the code simple and maintainable.
Pair programming Developers work in pairs, checking each other’s work and providing the support
to always do a good job.
Collective ownership The pairs of developers work on all areas of the system, so that no islands of
expertise develop and all the developers take responsibility for all of the code.
Anyone can change anything.
Continuous integration As soon as the work on a task is complete, it is integrated into the whole system.
After any such integration, all the unit tests in the system must pass.
Sustainable pace Large amounts of overtime are not considered acceptable as the net effect is
often to reduce code quality and medium term productivity
On-site customer A representative of the end-user of the system (the Customer) should be
available full time for the use of the XP team. In an extreme programming
process, the customer is a member of the development team and is responsible
for bringing system requirements to the team for implementation.
health care patient management system is shown in Figure 3.5. This is a short
Figure 3.4 Extreme
programming practices description of a scenario for prescribing medication for a patient.
The story cards are the main inputs to the XP planning process or the ‘planning
game’. Once the story cards have been developed, the development team breaks these
down into tasks (Figure 3.6) and estimates the effort and resources required for imple-
menting each task. This usually involves discussions with the customer to refine the
requirements. The customer then prioritizes the stories for implementation, choosing
those stories that can be used immediately to deliver useful business support. The
intention is to identify useful functionality that can be implemented in about two
weeks, when the next release of the system is made available to the customer.
Of course, as requirements change, the unimplemented stories change or may be
discarded. If changes are required for a system that has already been delivered, new
story cards are developed and again, the customer decides whether these changes
should have priority over new functionality.