Page 170 - Software and Systems Requirements Engineering in Practice
P. 170
136 S o f t w a r e & S y s t e m s R e q u i r e m e n t s E n g i n e e r i n g : I n P r a c t i c e
With these examples in mind, we summarize four related terms:
• Quality Fitness for one or more defined uses
• Quality attribute A property of the system or the process
that is indicative of quality
• Quality attribute measure A way of measuring a quality
attribute for a specific system or process
• Quality attribute requirement A requirement expressed in
terms of one or more quality attribute measures
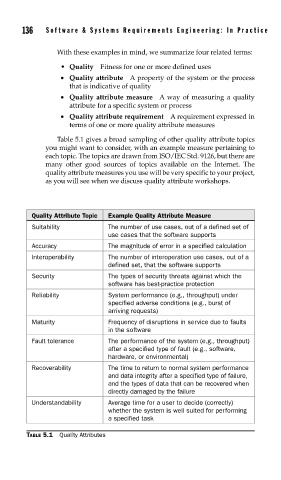
Table 5.1 gives a broad sampling of other quality attribute topics
you might want to consider, with an example measure pertaining to
each topic. The topics are drawn from ISO/IEC Std. 9126, but there are
many other good sources of topics available on the Internet. The
quality attribute measures you use will be very specific to your project,
as you will see when we discuss quality attribute workshops.
Quality Attribute Topic Example Quality Attribute Measure
Suitability The number of use cases, out of a defined set of
use cases that the software supports
Accuracy The magnitude of error in a specified calculation
Interoperability The number of interoperation use cases, out of a
defined set, that the software supports
Security The types of security threats against which the
software has best-practice protection
Reliability System performance (e.g., throughput) under
specified adverse conditions (e.g., burst of
arriving requests)
Maturity Frequency of disruptions in service due to faults
in the software
Fault tolerance The performance of the system (e.g., throughput)
after a specified type of fault (e.g., software,
hardware, or environmental)
Recoverability The time to return to normal system performance
and data integrity after a specified type of failure,
and the types of data that can be recovered when
directly damaged by the failure
Understandability Average time for a user to decide (correctly)
whether the system is well suited for performing
a specified task
TABLE 5.1 Quality Attributes