Page 105 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 105
92 3 Soil Erosion by Water
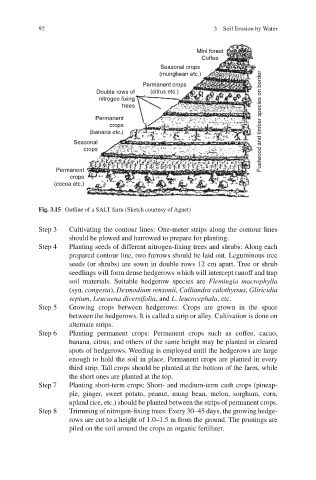
Mini forest
Coffee
Seasonal crops
(mungbean etc.)
Permanent crops
Double rows of (citrus etc.)
nitrogen fixing
trees
Permanent Fuelwood and timber species on border
crops
(banana etc.)
Seasonal
crops
Permanent
crops
(cocoa etc.)
Fig. 3.15 Outline of a SALT farm (Sketch courtesy of Agnet)
Step 3 Cultivating the contour lines: One-meter strips along the contour lines
should be plowed and harrowed to prepare for planting.
Step 4 Planting seeds of different nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs: Along each
prepared contour line, two furrows should be laid out. Leguminous tree
seeds (or shrubs) are sown in double rows 12 cm apart. Tree or shrub
seedlings will form dense hedgerows which will intercept runoff and trap
soil materials. Suitable hedgerow species are Flemingia macrophylla
(syn. congesta ), Desmodium rensonii , Calliandra calothyrsus , Gliricidia
sepium , Leucaena diversifolia , and L. leucocephala , etc.
Step 5 Growing crops between hedgerows: Crops are grown in the space
between the hedgerows. It is called a strip or alley. Cultivation is done on
alternate strips.
Step 6 Planting permanent crops: Permanent crops such as coffee, cacao,
banana, citrus, and others of the same height may be planted in cleared
spots of hedgerows. Weeding is employed until the hedgerows are large
enough to hold the soil in place. Permanent crops are planted in every
third strip. Tall crops should be planted at the bottom of the farm, while
the short ones are planted at the top.
Step 7 Planting short-term crops: Short- and medium-term cash crops (pineap-
ple, ginger, sweet potato, peanut, mung bean, melon, sorghum, corn,
upland rice, etc.) should be planted between the strips of permanent crops.
Step 8 Trimming of nitrogen-fixing trees: Every 30–45 days, the growing hedge-
rows are cut to a height of 1.0–1.5 m from the ground. The prunings are
piled on the soil around the crops as organic fertilizer.