Page 111 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 111
98 3 Soil Erosion by Water
CUT
FILL
ORIGINAL LAND
PROFILE
FILL
CUT
CUT
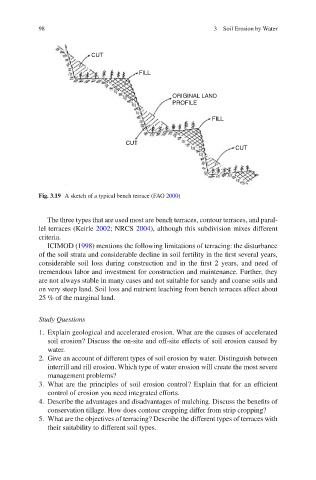
Fig. 3.19 A sketch of a typical bench terrace (FAO 2000 )
The three types that are used most are bench terraces, contour terraces, and paral-
lel terraces (Keirle 2002 ; NRCS 2004 ), although this subdivision mixes different
criteria.
ICIMOD ( 1998 ) mentions the following limitations of terracing: the disturbance
of the soil strata and considerable decline in soil fertility in the first several years,
considerable soil loss during construction and in the first 2 years, and need of
tremendous labor and investment for construction and maintenance. Further, they
are not always stable in many cases and not suitable for sandy and coarse soils and
on very steep land. Soil loss and nutrient leaching from bench terraces affect about
25 % of the marginal land.
Study Questions
1. Explain geological and accelerated erosion. What are the causes of accelerated
soil erosion? Discuss the on-site and off-site effects of soil erosion caused by
water.
2. Give an account of different types of soil erosion by water. Distinguish between
interrill and rill erosion. Which type of water erosion will create the most severe
management problems?
3. What are the principles of soil erosion control? Explain that for an effi cient
control of erosion you need integrated efforts.
4. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of mulching. Discuss the benefi ts of
conservation tillage. How does contour cropping differ from strip cropping?
5. What are the objectives of terracing? Describe the different types of terraces with
their suitability to different soil types.