Page 273 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 273
260 Soil and Water Contamination
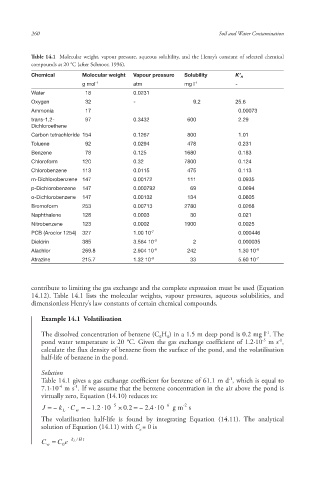
Table 14.1 Molecular weight, vapour pressure , aqueous solubility , and the Henry’s constant of selected chemical
compounds at 20 °C (after Schnoor, 1996).
Chemical Molecular weight Vapour pressure Solubility K’ H
g mol -1 atm mg l -1 -
Water 18 0.0231
Oxygen 32 - 9.2 25.6
Ammonia 17 0.00073
trans-1,2- 97 0.3432 600 2.29
Dichloroethene
Carbon tetrachloride 154 0.1267 800 1.01
Toluene 92 0.0294 478 0.231
Benzene 78 0.125 1680 0.183
Chloroform 120 0.32 7800 0.124
Chlorobenzene 113 0.0115 475 0.113
m-Dichlorobenzene 147 0.00172 111 0.0935
p-Dichlorobenzene 147 0.000792 69 0.0694
o-Dichlorobenzene 147 0.00132 134 0.0605
Bromoform 253 0.00713 2780 0.0268
Naphthalene 128 0.0003 30 0.021
Nitrobenzene 123 0.0002 1900 0.0025
PCB (Aroclor 1254) 327 1.00 10 -7 0.000446
Dieldrin 385 3.564 10 -9 2 0.000035
Alachlor 269.8 2.904 10 -8 242 1.30 10 -6
Atrazine 215.7 1.32 10 -9 33 5.60 10 -7
contribute to limiting the gas exchange and the complete expression must be used (Equation
14.12). Table 14.1 lists the molecular weight s, vapour pressure s, aqueous solubilities, and
dimensionless Henry’s law constants of certain chemical compounds.
Example 14.1 Volatilisation
-1
The dissolved concentration of benzene (C H ) in a 1.5 m deep pond is 0.2 mg l . The
6 6
-5
-1
pond water temperature is 20 °C. Given the gas exchange coefficient of 1.2·10 m s ,
calculate the flux density of benzene from the surface of the pond, and the volatilisation
half-life of benzene in the pond.
Solution
-1
Table 14.1 gives a gas exchange coefficient for benzene of 61.1 m d , which is equal to
-4
-1
7.1·10 m s . If we assume that the benzene concentration in the air above the pond is
virtually zero, Equation (14.10) reduces to:
6
-2
J k C 2 . 1 10 5 2 . 0 4 . 2 10 g m s
L w
The volatilisation half-life is found by integrating Equation (14.11). The analytical
solution of Equation (14.11) with C = 0 is
a
C C 0 e k L / H t
w
10/1/2013 6:45:17 PM
Soil and Water.indd 272
Soil and Water.indd 272 10/1/2013 6:45:17 PM