Page 32 - Solar Power in Building Design The Engineer's Complete Design Resource
P. 32
2 SOLAR POWER SYSTEM PHYSICS
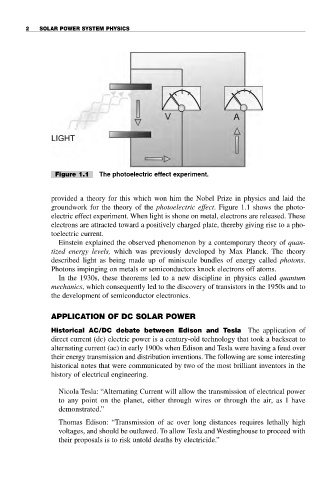
Figure 1.1 The photoelectric effect experiment.
provided a theory for this which won him the Nobel Prize in physics and laid the
groundwork for the theory of the photoelectric effect. Figure 1.1 shows the photo-
electric effect experiment. When light is shone on metal, electrons are released. These
electrons are attracted toward a positively charged plate, thereby giving rise to a pho-
toelectric current.
Einstein explained the observed phenomenon by a contemporary theory of quan-
tized energy levels, which was previously developed by Max Planck. The theory
described light as being made up of miniscule bundles of energy called photons.
Photons impinging on metals or semiconductors knock electrons off atoms.
In the 1930s, these theorems led to a new discipline in physics called quantum
mechanics, which consequently led to the discovery of transistors in the 1950s and to
the development of semiconductor electronics.
APPLICATION OF DC SOLAR POWER
Historical AC/DC debate between Edison and Tesla The application of
direct current (dc) electric power is a century-old technology that took a backseat to
alternating current (ac) in early 1900s when Edison and Tesla were having a feud over
their energy transmission and distribution inventions. The following are some interesting
historical notes that were communicated by two of the most brilliant inventors in the
history of electrical engineering.
Nicola Tesla: “Alternating Current will allow the transmission of electrical power
to any point on the planet, either through wires or through the air, as I have
demonstrated.”
Thomas Edison: “Transmission of ac over long distances requires lethally high
voltages, and should be outlawed. To allow Tesla and Westinghouse to proceed with
their proposals is to risk untold deaths by electricide.”