Page 80 - Solar Power in Building Design The Engineer's Complete Design Resource
P. 80
50 SOLAR POWER SYSTEM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
protected with a forward-biased diode connected to the positive output of individual
solar panels (not shown in Figure 3.2).
An appropriate surge protector connected between the positive and negative supply
provides protection against lightning surges, which could damage the solar array
system components. In order to provide equipment-grounding bias, the chassis or
enclosures of all PV modules and the dc motor pump are tied together by means of
grounding clamps. The system ground is in turn connected to an appropriate ground-
ing rod. All PV interconnecting wires are sized and the proper type selected to
prevent power losses caused by a number of factors, such as exposure to the sun,
excessive wire resistance, and additional requirements that are mandated by the NEC.
The photovoltaic solar system described is typically used as an agricultural appli-
cation, where either regular electrical service is unavailable or the cost is prohibitive.
A floating or submersible dc pump connected to a dc PV array can provide a constant
stream of well water that can be accumulated in a reservoir for farm or agricultural
use. In subsequent sections we will discuss the specifications and use of all system
components used in solar power cogeneration applications.
STAND-ALONE DC SOLAR POWER SYSTEM
WITH BATTERY BACKUP
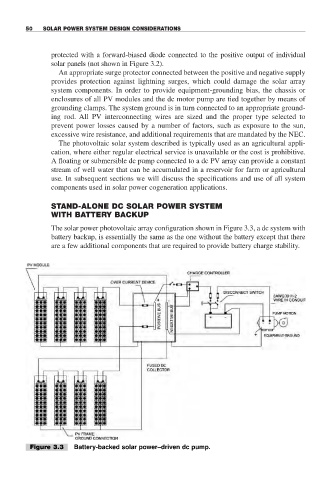
The solar power photovoltaic array configuration shown in Figure 3.3, a dc system with
battery backup, is essentially the same as the one without the battery except that there
are a few additional components that are required to provide battery charge stability.
Figure 3.3 Battery-backed solar power–driven dc pump.