Page 90 - Solar Power in Building Design The Engineer's Complete Design Resource
P. 90
60 SOLAR POWER SYSTEM DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
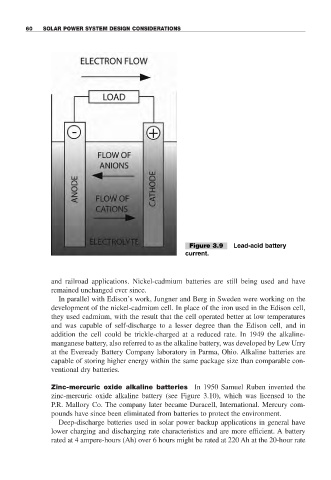
Figure 3.9 Lead-acid battery
current.
and railroad applications. Nickel-cadmium batteries are still being used and have
remained unchanged ever since.
In parallel with Edison’s work, Jungner and Berg in Sweden were working on the
development of the nickel-cadmium cell. In place of the iron used in the Edison cell,
they used cadmium, with the result that the cell operated better at low temperatures
and was capable of self-discharge to a lesser degree than the Edison cell, and in
addition the cell could be trickle-charged at a reduced rate. In 1949 the alkaline-
manganese battery, also referred to as the alkaline battery, was developed by Lew Urry
at the Eveready Battery Company laboratory in Parma, Ohio. Alkaline batteries are
capable of storing higher energy within the same package size than comparable con-
ventional dry batteries.
Zinc-mercuric oxide alkaline batteries In 1950 Samuel Ruben invented the
zinc-mercuric oxide alkaline battery (see Figure 3.10), which was licensed to the
P.R. Mallory Co. The company later became Duracell, International. Mercury com-
pounds have since been eliminated from batteries to protect the environment.
Deep-discharge batteries used in solar power backup applications in general have
lower charging and discharging rate characteristics and are more efficient. A battery
rated at 4 ampere-hours (Ah) over 6 hours might be rated at 220 Ah at the 20-hour rate