Page 56 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 56
Differential and Integral Calculus 45
and the process may be repeated, as in
I {I [I f(x)dxldxldx + ISlf(x)dx.9
Definite multiple integrals are solved from the inner integral to the outer.
The double integral of a function with two independent variables is of the
form
SI f(x,y)dy dx = I [I f(x,y)dyIdx
where the limits of the inner integral are functions of x or constants as in the
definite integral
where a and b may be f,(x) and f,(x).
Second Fundamental Theorem
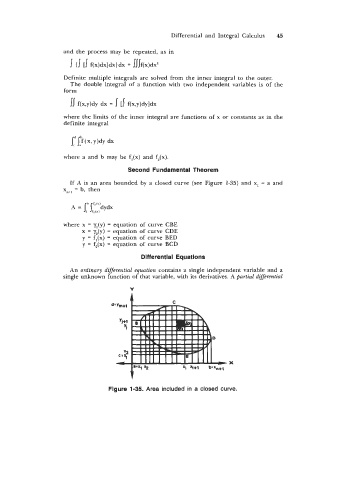
If A is an area bounded by a closed curve (see Figure 1-35) and x, = a and
x”+~ b, then
=
where x = y,(y) = equation of curve CBE
x = y,(y) = equation of curve CDE
y = f,(x) = equation of curve BED
y = f,(x) = equation of curve BCD
Differential Equations
An ordinary differential equation contains a single independent variable and a
single unknown function of that variable, with its derivatives. A partial differential
V
X
Figure 1-35. Area included in a closed curve.