Page 340 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 340
314 Chapter Fifteen
Basic formulas:
πDN
V b = V i = 224 h 1
− h 2 = 224 ΔH
720
where V b = pitch line (blade) velocity, ft/s
D = pitch diameter of wheel, inches (base diameter plus
height of blade)
N = rotative speed, r/min
V j = steam jet velocity, ft/s
h 1 = inlet steam enthalpy, Btu/lb
h 2 = isentropic exhaust steam enthalpy, Btu/lb
h 2e = stage exit steam enthalpy, Btu/lb
ΔH = isentropic heat drop, Btu/lb (h 1 − h 2 )
V b /V j = velocity ratio, dimensionless
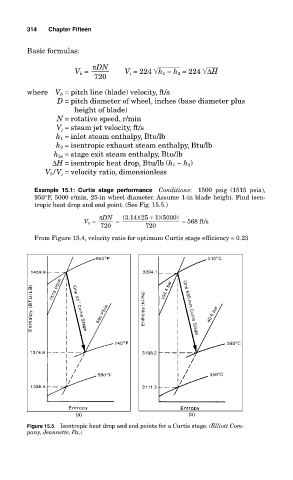
Example 15.1: Curtis stage performance Conditions: 1500 psig (1515 psia),
950°F, 5000 r/min, 25-in wheel diameter. Assume 1-in blade height. Find isen-
tropic heat drop and end point. (See Fig. 15.5.)
πDN (3.14)(25 + 1)(5000)
V b = = = 568 ft/s
720 720
From Figure 15.4, velocity ratio for optimum Curtis stage efficiency = 0.23
(a) (b)
Figure 15.5 Isentropic heat drop and end points for a Curtis stage. (Elliott Com-
pany, Jeannette, Pa.)