Page 170 -
P. 170
136 PART 2 • STRATEGY FORMULATION
evaluate strategies on items other than financial measures. This is the basic tenet of the
Balanced Scorecard. Financial measures and ratios are vitally important. However, of
equal importance are factors such as customer service, employee morale, product quality,
pollution abatement, business ethics, social responsibility, community involvement, and
other such items. In conjunction with financial measures, these “softer” factors comprise
an integral part of both the objective-setting process and the strategy-evaluation process.
These factors can vary by organization, but such items, along with financial measures,
comprise the essence of a Balanced Scorecard. A Balanced Scorecard for a firm is simply
a listing of all key objectives to work toward, along with an associated time dimension of
when each objective is to be accomplished, as well as a primary responsibility or contact
person, department, or division for each objective.
Types of Strategies
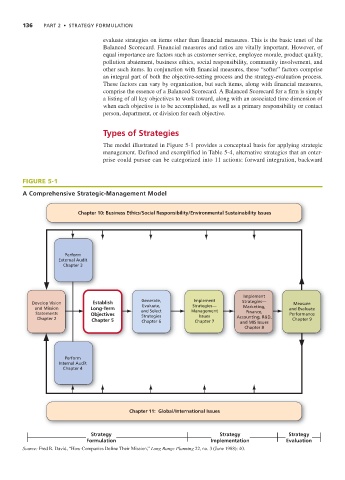
The model illustrated in Figure 5-1 provides a conceptual basis for applying strategic
management. Defined and exemplified in Table 5-4, alternative strategies that an enter-
prise could pursue can be categorized into 11 actions: forward integration, backward
FIGURE 5-1
A Comprehensive Strategic-Management Model
Chapter 10: Business Ethics/Social Responsibility/Environmental Sustainability Issues
Perform
External Audit
Chapter 3
Implement
Implement
Develop Vision Establish Generate, Strategies— Strategies— Measure
Evaluate,
and Mission Long-Term Marketing, and Evaluate
Statements Objectives and Select Management Finance, Performance
Strategies
Issues
Chapter 2 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Accounting, R&D, Chapter 9
and MIS Issues
Chapter 8
Perform
Internal Audit
Chapter 4
Chapter 11: Global/International Issues
Strategy Strategy Strategy
Formulation Implementation Evaluation
Source: Fred R. David, “How Companies Define Their Mission,” Long Range Planning 22, no. 3 (June 1988): 40.