Page 147 - Strategies and Applications in Quantum Chemistry From Molecular Astrophysics to Molecular Engineer
P. 147
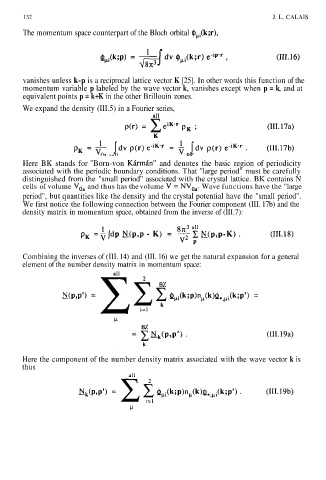
132 J. L. CALAIS
The momentum space counterpart of the Bloch orbital
vanishes unless k-p is a reciprocal lattice vector K [25]. In other words this function of the
momentum variable p labeled by the wave vector k, vanishes except when p = k, and at
equivalent points p = k+K in the other Brillouin zones.
We expand the density (III.5) in a Fourier series,
Here BK stands for "Born-von and denotes the basic region of periodicity
associated with the periodic boundary conditions. That "large period" must be carefully
distinguished from the "small period" associated with the crystal lattice. BK contains N
cells of volume and thus has the volume Wave functions have the "large
period", but quantities like the density and the crystal potential have the "small period".
We first notice the following connection between the Fourier component (III. 17b) and the
density matrix in momentum space, obtained from the inverse of (III.7):
Combining the inverses of (III. 14) and (III. 16) we get the natural expansion for a general
element of the number density matrix in momentum space:
Here the component of the number density matrix associated with the wave vector k is
thus