Page 188 - Strategies and Applications in Quantum Chemistry From Molecular Astrophysics to Molecular Engineer
P. 188
CORE-HOLE STATES AND THE KOOPMANS THEOREM 171
configuration with a core hole (which arise from differences of spin coupling between
the core and valence electrons) can readily be studied by using the optimized orbitals
for the configurational average energy to set up the secular equations that will lead
to the individual states.
Another application is to the study of the ‘Auger states’ in which a further electron
ionization of attachment may occur, leaving the system with holes in more than one
shell. Such states were considered in some detail by Firsht and McWeeny [9] for free
atoms: here we have made a preliminary application to the nitrogen molecule. The
initial aim is simply to identify and assign the principal peaks and satellites in the
Auger spectrum of gaseous
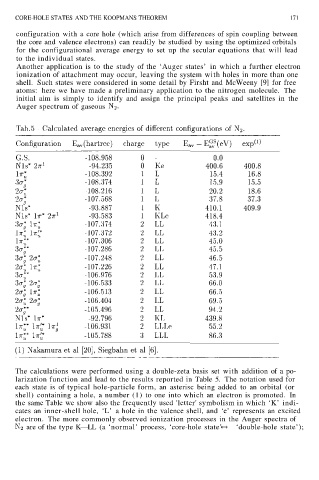
The calculations were performed using a double-zeta basis set with addition of a po-
larization function and lead to the results reported in Table 5. The notation used for
each state is of typical hole-particle form, an asterisc being added to an orbital (or
shell) containing a hole, a number (1) to one into which an electron is promoted. In
the same Table we show also the frequently used 'letter' symbolism in which ‘K’ indi-
cates an inner-shell hole, ‘L’ a hole in the valence shell, and ‘e’ represents an excited
electron. The more commonly observed ionization processes in the Auger spectra of
are of the type K—LL (a ‘normal’ process, ‘core-hole state’ ‘double-hole state’);