Page 190 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 190
Brockenbrough_Ch04.qxd 9/29/05 5:09 PM Page 4.18
BUILDING CODES, LOADS, AND FIRE PROTECTION*
4.18 CHAPTER FOUR
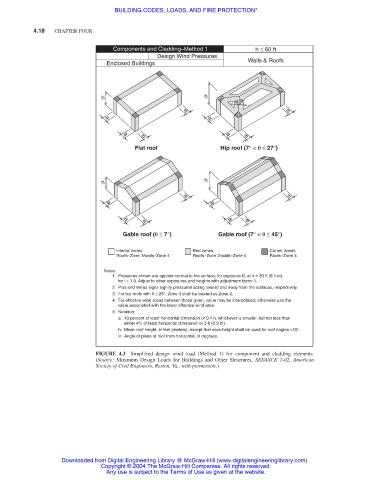
Components and Cladding–Method 1 h ≤ 60 ft
Design Wind Pressures
Enclosed Buildings Walls & Roofs
h h
a a
a a
a a
a a
a a
Flat roof Hip roof (7° < θ ≤ 27°)
h h
a a
a a
a a
a a
Gable roof (θ ≤ 7°) Gable roof (7° < θ ≤ 45°)
Interior zones End zones Corner zones
Roofs–Zone 1/walls–Zone 4 Roofs–Zone 2/walls–Zone 5 Roofs–Zone 3
Notes:
1. Pressures shown are applied normal to the surface, for exposure B, at h = 30 ft (9.1 m),
for l = 1.0. Adjust to other exposures and heights with adjustment factor λ.
2. Plus and minus signs signify pressures acting toward and away from the surfaces, respectively.
3. For hip roofs with θ ≤ 25°, Zone 3 shall be treated as Zone 2.
4. For effective wind areas between those given, value may be interpolated; otherwise use the
value associated with the lower effective wind area.
5. Notation:
a: 10 percent of least horizontal dimension or 0.4 h, whichever is smaller, but not less than
either 4% of least horizontal dimension or 3 ft (0.9 m).
h: Mean roof height, in feet (meters), except that eave height shall be used for roof angles <10°.
θ: Angle of plane of roof from horizontal, in degrees.
FIGURE 4.3 Simplified design wind load (Method 1) for component and cladding elements.
(Source: Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, SEI/ASCE 7-02, American
Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, Va., with permission.)
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.