Page 94 - Sumatra Geology, Resources and Tectonic Evolution
P. 94
PRE-TERTIARY VOLCANIC ROCKS 81
Island Arc is faulted, thrust and intruded by Late Cretaceous and Formation is thrust over the oceanic Babahrot Formation, and in
Tertiary granitoids. The component units of the Bentaro Arc are the Meukek River volcanics are transformed into amphibolites
described in the Banda Aceh and Calang Quadrangles by in the Meukek Gneiss Complex. Barber (2000) suggests these
Bennett et al. (1981a, b). Here the Bentaro Volcanic Formation garnet amphibolites represent rocks which were subducted,
is overlain by reef limestones and dark limestones (Lamno metamorphosed and subsequently tectonically exhumed.
Formation) with Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous fossils, and is Barber (2000) places the Sise Limestone Formation (reef lime-
faulted against and underlain by the Lhoong Formation. The stones) and the Kenyaran Volcanic Formation (epidotized basalts)
Raba Limestone Formation, composed of reef limestones and of the Takengon Quadrangle (Cameron et al. 1983) within the
thin bedded argillaceous and siliceous limestones is thrust over Island Arc Assemblage, from which it has been displaced by
the Lhoong Formation. Near the Sumatra Fault Zone the movements of the Sumatra Fault Zone.
Bentaro Arc is overthrust by the Geumpang Formation which
belongs to the Accretionary Complex. In the Calang Quadrangle
volcanics are not exposed, only reef limestones of the Teunom
Formation are seen.
Barber (2000) includes the Tapaktuan Volcanic Formation
which crops out in the coastal plain of the Tapaktuan Quadrangle
(Cameron et al. 1982b) within the Bentaro Arc. The Tapaktuan Gumai Mountains (refer to Fig. 4.19)
Volcanic Formation crops out as fault lozenges in the Kluet
Fault Complex. In the NW of the main outcrop, the Tapaktuan
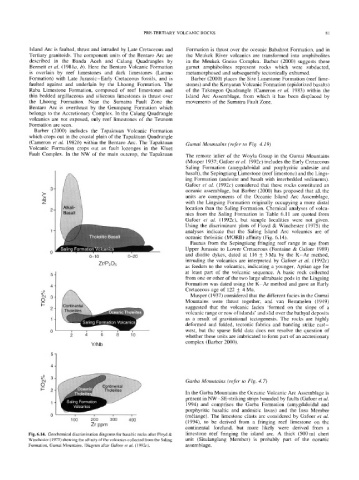
The remote inlier of the Woyla Group in the Gumai Mountains
(Musper 1937; Gafoer et al. 1992c) includes the Early Cretaceous
Saling Formation (amygdaloidal and porphyritic andesite and
basalt), the Sepingtiang Limestone (reef limestone) and the Lings-
ing Formation (andesite and basalt with interbedded sediments).
Gafoer et al. (1992c) considered that these rocks constituted an
3 oceanic assemblage, but Barber (2000) has proposed that all the
>-
units are components of the Oceanic Island Arc Assemblage,
_Q
z with the Lingsing Formation originally occupying a more distal
location than the Saling Formation. Chemical analyses of volca-
2
nics from the Saling Formation in Table 6.11 are quoted from
Gafoer et al. (1992c), but sample localities were not given.
Using the discriminant plots of Floyd & Winchester (1975) the
analyses indicate that the Saling Island Arc volcanics are of
oceanic tholeiitic (MORB) affinity (Fig. 6.14).
Faunas from the Sepingtiang fringing reef range in age from
Upper Jurassic to Lower Cretaceous (Fontaine & Gafoer 1989)
0-10 0-20 and diorite dykes, dated at 116 _+ 3 Ma by the K-Ar method,
intruding the volcanics are interpreted by Gafoer et al. (1992c)
Zr/P205
as feeders to the volcanics, indicating a younger, Aptian age for
at least part of the volcanic sequence. A basic rock collected
from one or other of the two large ultrabasic pods in the Lingsing
Formation was dated using the K-Ar method and gave an Early
4
Cretaceous age of 122 ___ 4 Ma.
o~
o4 3 Musper (1937) considered that the different facies in the Gumai
0 Mountains were thrust together, and van Bemmelen (1949)
I--
2 suggested that the volcanic facies 'formed on the slope of a
V as a result of gravitational tectogenesis. The rocks are highly
volcanic range or row of islands' and slid over the bathyal deposits
deformed and folded, tectonic fabrics and banding strike east-
;2 ,~ 6 8 10 west, but the sparse field data does not resolve the question of
whether these units are imbricated to form part of an accretionary
Y/Nb complex (Barber 2000).
Garba Mountains (refer to Fig. 4.7)
o
In the Garba Mountains the Oceanic Volcanic Arc Assemblage is
present in NW-SE-striking strips bounded by faults (Gafoer et al.
1994) and comprises the Garba Formation (amygdaloidal and
porphyritic basaltic and andesitic lavas) and the Insu Member
(m61ange). The limestone clasts are considered by Gafoer et al.
1 0 0 200 3 0 0 ' 400
'
Zr ppm (1994), to be derived from a fringing reef limestone on the
continental foreland, but more likely were derived from a
Fig. 6.14. Geochemical discrimination diagrams for basaltic rocks after Floyd & limestone reef fringing the island arc. A thick (500 m) chert
Winchester (1975) showing the affinity of the volcanics collected from the Saling unit (Situlanglang Member) is probably part of the oceanic
Formation, Gumai Mountains. Diagram after Gafoer et al. (1992c). assemblage.