Page 148 - Sustainability Communication Interdisciplinary Perspectives and Theoritical Foundations
P. 148
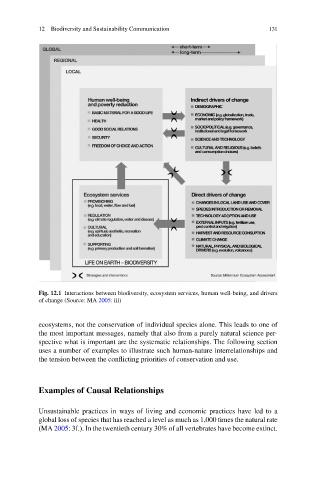
12 Biodiversity and Sustainability Communication 131
Fig. 12.1 Interactions between biodiversity, ecosystem services, human well-being, and drivers
of change (Source: MA 2005: iii)
ecosystems, not the conservation of individual species alone. This leads to one of
the most important messages, namely that also from a purely natural science per-
spective what is important are the systematic relationships. The following section
uses a number of examples to illustrate such human-nature interrelationships and
the tension between the conflicting priorities of conservation and use.
Examples of Causal Relationships
Unsustainable practices in ways of living and economic practices have led to a
global loss of species that has reached a level as much as 1,000 times the natural rate
(MA 2005: 3f.). In the twentieth century 30% of all vertebrates have become extinct.