Page 247 - Synthetic Fuels Handbook
P. 247
FUELS FROM BIOMASS 233
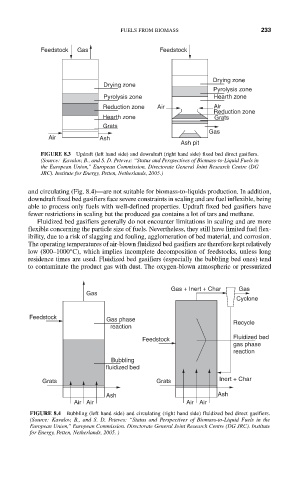
Feedstock Gas Feedstock
Drying zone
Drying zone
Pyrolysis zone
Pyrolysis zone Hearth zone
Reduction zone Air Air
Reduction zone
Hearth zone Grats
Grats
Gas
Air Ash
Ash pit
FIGURE 8.3 Updraft (left hand side) and downdraft (right hand side) fixed bed direct gasifiers.
(Source: Kavalov, B., and S. D. Peteves: “Status and Perspectives of Biomass-to-Liquid Fuels in
the European Union,” European Commission. Directorate General Joint Research Centre (DG
JRC). Institute for Energy, Petten, Netherlands, 2005.)
and circulating (Fig. 8.4)—are not suitable for biomass-to-liquids production. In addition,
downdraft fixed bed gasifiers face severe constraints in scaling and are fuel inflexible, being
able to process only fuels with well-defined properties. Updraft fixed bed gasifiers have
fewer restrictions in scaling but the produced gas contains a lot of tars and methane.
Fluidized bed gasifiers generally do not encounter limitations in scaling and are more
flexible concerning the particle size of fuels. Nevertheless, they still have limited fuel flex-
ibility, due to a risk of slagging and fouling, agglomeration of bed material, and corrosion.
The operating temperatures of air-blown fluidized bed gasifiers are therefore kept relatively
low (800–1000°C), which implies incomplete decomposition of feedstocks, unless long
residence times are used. Fluidized bed gasifiers (especially the bubbling bed ones) tend
to contaminate the product gas with dust. The oxygen-blown atmospheric or pressurized
Gas + Inert + Char Gas
Gas
Cyclone
Feedstock
Gas phase
Recycle
reaction
Feedstock Fluidized bed
gas phase
reaction
Bubbling
fluidized bed
Grats Grats Inert + Char
Ash Ash
Air Air Air Air
FIGURE 8.4 Bubbling (left hand side) and circulating (right hand side) fluidized bed direct gasifiers.
(Source: Kavalov, B., and S. D. Peteves: “Status and Perspectives of Biomass-to-Liquid Fuels in the
European Union,” European Commission. Directorate General Joint Research Centre (DG JRC). Institute
for Energy, Petten, Netherlands, 2005. )