Page 127 -
P. 127
112 GIORGINI, KOLP, AND MYLOPOULOS
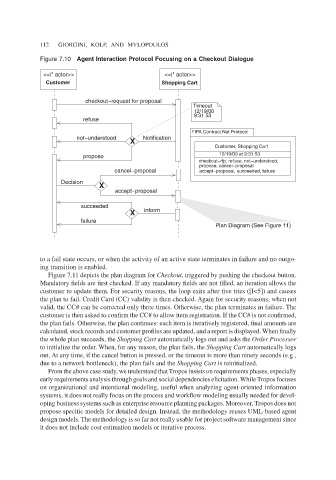
Figure 7.10 Agent Interaction Protocol Focusing on a Checkout Dialogue
<<i* actor>> <<i* actor>>
Customer Shopping Cart
checkout−request for proposal
Timeout
12/19/00
refuse 9:31 53
FIPA Contract Net Protocol
not−understood Notification
X
Customer, Shopping Cart
propose 12/19/00 at 9:31 53
checkout−rfp, refuse, not−understood,
propose, cancel−proposal
cancel−proposal accept−proposal, succeeded, failure
Decision
X
accept−proposal
succeeded
X inform
failure
Plan Diagram (See Figure 11)
to a fail state occurs, or when the activity of an active state terminates in failure and no outgo-
ing transition is enabled.
Figure 7.11 depicts the plan diagram for Checkout, triggered by pushing the checkout button.
Mandatory fields are first checked. If any mandatory fields are not filled, an iteration allows the
customer to update them. For security reasons, the loop exits after five tries ([I<5]) and causes
the plan to fail. Credit Card (CC) validity is then checked. Again for security reasons, when not
valid, the CC# can be corrected only three times. Otherwise, the plan terminates in failure. The
customer is then asked to confirm the CC# to allow item registration. If the CC# is not confirmed,
the plan fails. Otherwise, the plan continues: each item is iteratively registered, final amounts are
calculated, stock records and customer profiles are updated, and a report is displayed. When finally
the whole plan succeeds, the Shopping Cart automatically logs out and asks the Order Processor
to initialize the order. When, for any reason, the plan fails, the Shopping Cart automatically logs
out. At any time, if the cancel button is pressed, or the timeout is more than ninety seconds (e.g.,
due to a network bottleneck), the plan fails and the Shopping Cart is reinitialized.
From the above case study, we understand that Tropos insists on requirements phases, especially
early requirements analysis through goals and social dependencies elicitation. While Tropos focuses
on organizational and intentional modeling, useful when analyzing agent-oriented information
systems, it does not really focus on the process and workflow modeling usually needed for devel-
oping business systems such as enterprise resource planning packages. Moreover, Tropos does not
propose specific models for detailed design. Instead, the methodology reuses UML-based agent
design models. The methodology is so far not really usable for project software management since
it does not include cost estimation models or iterative process.