Page 140 -
P. 140
AGENT-ORIENTED METHODS AND METHOD ENGINEERING 125
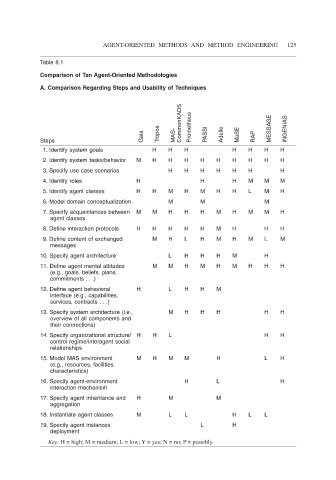
Table 8.1
Comparison of Ten Agent-Oriented Methodologies
A. Comparison Regarding Steps and Usability of Techniques
CommonKADS Prometheus MESSAGE INGENIAS
Gaia Tropos MAS- PASSI Adelfe MaSE RAP
Steps
1. Identify system goals H H H H H H H
2. Identify system tasks/behavior M H H H H H H H H H
3. Specify use case scenarios H H H H H H H
4. Identify roles H H H M M M
5. Identify agent classes H H M H M H H L M H
6. Model domain conceptualization M M M
7. Specify acquaintances between M M H H H M H M M H
agent classes
8. Define interaction protocols H H H H H M H H H
9. Define content of exchanged M H L H M H M L M
messages
10. Specify agent architecture L H H H M H
11. Define agent mental attitudes M M H M H M H H H
(e.g., goals, beliefs, plans,
commitments . . .)
12. Define agent behavioral H L H H M
interface (e.g., capabilities,
services, contracts . . .)
13. Specify system architecture (i.e., M H H H H H
overview of all components and
their connections)
14. Specify organizational structure/ H H L H H
control regime/interagent social
relationships
15. Model MAS environment M H M M H L H
(e.g., resources, facilities,
characteristics)
16. Specify agent-environment H L H
interaction mechanism
17. Specify agent inheritance and H M M
aggregation
18. Instantiate agent classes M L L H L L
19. Specify agent instances L H
deployment
Key: H = high; M = medium; L = low; Y = yes; N = no; P = possibly.