Page 309 -
P. 309
276 Part 3 • the analysis Process
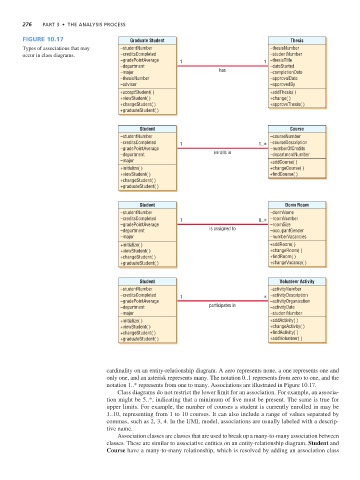
Figure 10.17 Graduate Student Thesis
Types of associations that may –studentNumber –thesisNumber
occur in class diagrams. –creditsCompleted –studentNumber
–gradePointAverage 1 1 –thesisTitle
–department –dateStarted
–major has –completionDate
–thesisNumber –approvalDate
–advisor –approvedBy
+acceptStudent( ) +addThesis( )
+viewStudent( ) +change( )
+changeStudent( ) +approveThesis( )
+graduateStudent( )
Student Course
–studentNumber –courseNumber
–creditsCompleted 1 1.. –courseDescription
–gradePointAverage –numberOfCredits
–department enrolls in –departmentNumber
–major +addCourse( )
+initialize( ) +changeCourse( )
+viewStudent( ) +findCourse( )
+changeStudent( )
+graduateStudent( )
Student Dorm Room
–studentNumber –dormName
–creditsCompleted 1 0.. –roomNumber
–gradePointAverage –roomSize
–department is assigned to –occupantGender
–major –numberVacancies
+initialize( ) +addRoom( )
+viewStudent( ) +changeRoom( )
+changeStudent( ) +findRoom( )
+graduateStudent( ) +changeVacancy( )
Student Volunteer Activity
–studentNumber –activityNumber
–creditsCompleted 1 –activityDescription
–gradePointAverage –activityOrganization
–department participates in –activityDate
–major –studentNumber
+initialize( ) +addActivity( )
+viewStudent( ) +changeActivity( )
+changeStudent( ) +findActivity( )
+graduateStudent( ) +addVolunteer( )
cardinality on an entity-relationship diagram. A zero represents none, a one represents one and
only one, and an asterisk represents many. The notation 0..1 represents from zero to one, and the
notation 1..* represents from one to many. Associations are illustrated in Figure 10.17.
Class diagrams do not restrict the lower limit for an association. For example, an associa-
tion might be 5..*, indicating that a minimum of five must be present. The same is true for
upper limits. For example, the number of courses a student is currently enrolled in may be
1..10, representing from 1 to 10 courses. It can also include a range of values separated by
commas, such as 2, 3, 4. In the UML model, associations are usually labeled with a descrip-
tive name.
Association classes are classes that are used to break up a many-to-many association between
classes. These are similar to associative entities on an entity-relationship diagram. Student and
Course have a many-to-many relationship, which is resolved by adding an association class