Page 47 -
P. 47
14 Part 1 • SyStemS analySiS FundamentalS
Figure 1.6 Begin Object-Oriented
Analysis and Design
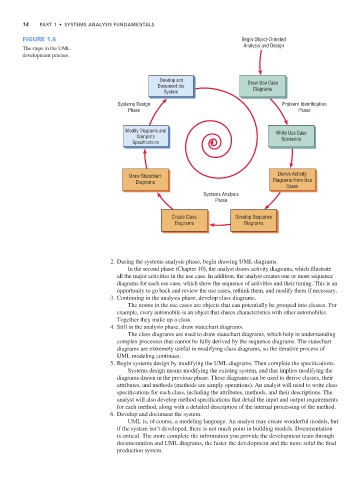
The steps in the UML
development process.
Develop and Draw Use Case
Document the Diagrams
System
Systems Design Problem Identification
Phase Phase
Modify Diagrams and Write Use Case
Complete Scenarios
Specifications
Draw Statechart Derive Activity
Diagrams Diagrams from Use
Cases
Systems Analysis
Phase
Create Class Develop Sequence
Diagrams Diagrams
2. During the systems analysis phase, begin drawing UML diagrams.
In the second phase (Chapter 10), the analyst draws activity diagrams, which illustrate
all the major activities in the use case. In addition, the analyst creates one or more sequence
diagrams for each use case, which show the sequence of activities and their timing. This is an
opportunity to go back and review the use cases, rethink them, and modify them if necessary.
3. Continuing in the analysis phase, develop class diagrams.
The nouns in the use cases are objects that can potentially be grouped into classes. For
example, every automobile is an object that shares characteristics with other automobiles.
Together they make up a class.
4. Still in the analysis phase, draw statechart diagrams.
The class diagrams are used to draw statechart diagrams, which help in understanding
complex processes that cannot be fully derived by the sequence diagrams. The statechart
diagrams are extremely useful in modifying class diagrams, so the iterative process of
UML modeling continues.
5. Begin systems design by modifying the UML diagrams. Then complete the specifications.
Systems design means modifying the existing system, and that implies modifying the
diagrams drawn in the previous phase. These diagrams can be used to derive classes, their
attributes, and methods (methods are simply operations). An analyst will need to write class
specifications for each class, including the attributes, methods, and their descriptions. The
analyst will also develop method specifications that detail the input and output requirements
for each method, along with a detailed description of the internal processing of the method.
6. Develop and document the system.
UML is, of course, a modeling language. An analyst may create wonderful models, but
if the system isn’t developed, there is not much point in building models. Documentation
is critical. The more complete the information you provide the development team through
documentation and UML diagrams, the faster the development and the more solid the final
production system.