Page 66 -
P. 66
ChaPter 2 • underStanding and modeling organizational SyStemS 33
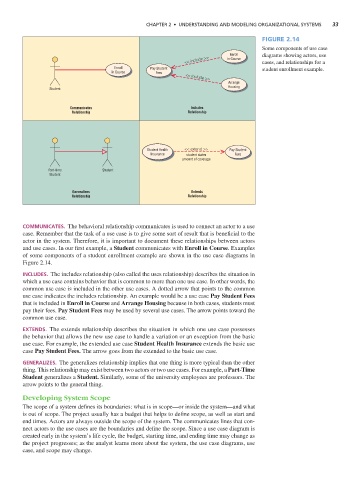
Figure 2.14
Some components of use case
Enroll diagrams showing actors, use
<< include >> in Course cases, and relationships for a
Enroll Pay Student student enrollment example.
in Course Fees
<< include >>
Arrange
Student Housing
Communicates Includes
Relationship Relationship
Student Health << extend >> Pay Student
Insurance student states Fees
amount of coverage
Part-time Student
Student
Generalizes Extends
Relationship Relationship
CommuniCates. The behavioral relationship communicates is used to connect an actor to a use
case. Remember that the task of a use case is to give some sort of result that is beneficial to the
actor in the system. Therefore, it is important to document these relationships between actors
and use cases. In our first example, a Student communicates with Enroll in Course. Examples
of some components of a student enrollment example are shown in the use case diagrams in
Figure 2.14.
inCludes. The includes relationship (also called the uses relationship) describes the situation in
which a use case contains behavior that is common to more than one use case. In other words, the
common use case is included in the other use cases. A dotted arrow that points to the common
use case indicates the includes relationship. An example would be a use case Pay Student Fees
that is included in Enroll in Course and Arrange Housing because in both cases, students must
pay their fees. Pay Student Fees may be used by several use cases. The arrow points toward the
common use case.
extends. The extends relationship describes the situation in which one use case possesses
the behavior that allows the new use case to handle a variation or an exception from the basic
use case. For example, the extended use case Student Health Insurance extends the basic use
case Pay Student Fees. The arrow goes from the extended to the basic use case.
Generalizes. The generalizes relationship implies that one thing is more typical than the other
thing. This relationship may exist between two actors or two use cases. For example, a Part-Time
Student generalizes a Student. Similarly, some of the university employees are professors. The
arrow points to the general thing.
Developing System Scope
The scope of a system defines its boundaries: what is in scope—or inside the system—and what
is out of scope. The project usually has a budget that helps to define scope, as well as start and
end times. Actors are always outside the scope of the system. The communicates lines that con-
nect actors to the use cases are the boundaries and define the scope. Since a use case diagram is
created early in the system’s life cycle, the budget, starting time, and ending time may change as
the project progresses; as the analyst learns more about the system, the use case diagrams, use
case, and scope may change.