Page 112 - Tandem Techniques
P. 112
Page 93
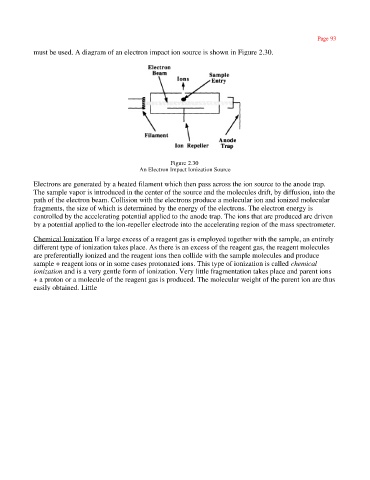
must be used. A diagram of an electron impact ion source is shown in Figure 2.30.
Figure 2.30
An Electron Impact Ionization Source
Electrons are generated by a heated filament which then pass across the ion source to the anode trap.
The sample vapor is introduced in the center of the source and the molecules drift, by diffusion, into the
path of the electron beam. Collision with the electrons produce a molecular ion and ionized molecular
fragments, the size of which is determined by the energy of the electrons. The electron energy is
controlled by the accelerating potential applied to the anode trap. The ions that are produced are driven
by a potential applied to the ion-repeller electrode into the accelerating region of the mass spectrometer.
Chemical Ionization If a large excess of a reagent gas is employed together with the sample, an entirely
different type of ionization takes place. As there is an excess of the reagent gas, the reagent molecules
are preferentially ionized and the reagent ions then collide with the sample molecules and produce
sample + reagent ions or in some cases protonated ions. This type of ionization is called chemical
ionization and is a very gentle form of ionization. Very little fragmentation takes place and parent ions
+ a proton or a molecule of the reagent gas is produced. The molecular weight of the parent ion are thus
easily obtained. Little