Page 74 - The Definitive Guide to Building Java Robots
P. 74
Preston_5564C03.fm Page 55 Wednesday, October 5, 2005 7:21 AM
CHAPTER 3 ■ MOTION 55
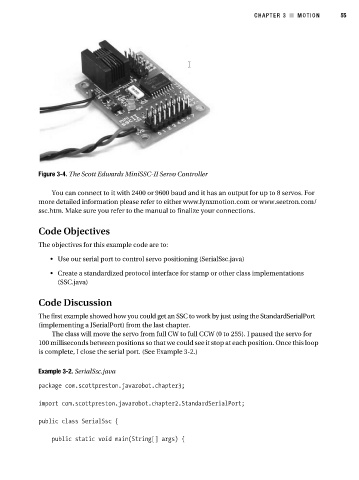
Figure 3-4. The Scott Edwards MiniSSC-II Servo Controller
You can connect to it with 2400 or 9600 baud and it has an output for up to 8 servos. For
more detailed information please refer to either www.lynxmotion.com or www.seetron.com/
ssc.htm. Make sure you refer to the manual to finalize your connections.
Code Objectives
The objectives for this example code are to:
• Use our serial port to control servo positioning (SerialSsc.java)
• Create a standardized protocol interface for stamp or other class implementations
(SSC.java)
Code Discussion
The first example showed how you could get an SSC to work by just using the StandardSerialPort
(implementing a JSerialPort) from the last chapter.
The class will move the servo from full CW to full CCW (0 to 255). I paused the servo for
100 milliseconds between positions so that we could see it stop at each position. Once this loop
is complete, I close the serial port. (See Example 3-2.)
Example 3-2. SerialSsc.java
package com.scottpreston.javarobot.chapter3;
import com.scottpreston.javarobot.chapter2.StandardSerialPort;
public class SerialSsc {
public static void main(String[] args) {