Page 83 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 83
70 I n t e g r a t e d P l a n n i n g S t r a t e g i c P l a n n i n g 71
External Internal
appraisal appraisal
Threats and Strengths and
opportunities in weakness of
environment organization
Key success Distinctive
factors competences
Creation
Social of Managerial
responsibility strategy values
Evaluation
and choice
of
strategy
Implementation
of strategy
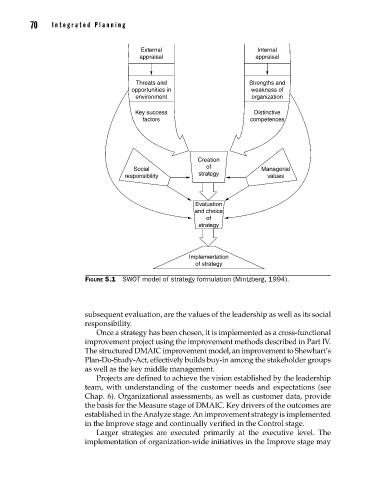
Figure 5.1 SWOT model of strategy formulation (Mintzberg, 1994).
subsequent evaluation, are the values of the leadership as well as its social
responsibility.
Once a strategy has been chosen, it is implemented as a cross-functional
improvement project using the improvement methods described in Part IV.
The structured DMAIC improvement model, an improvement to Shewhart’s
Plan-Do-Study-Act, effectively builds buy-in among the stakeholder groups
as well as the key middle management.
Projects are defined to achieve the vision established by the leadership
team, with understanding of the customer needs and expectations (see
Chap. 6). Organizational assessments, as well as customer data, provide
the basis for the Measure stage of DMAIC. Key drivers of the outcomes are
established in the Analyze stage. An improvement strategy is implemented
in the Improve stage and continually verified in the Control stage.
Larger strategies are executed primarily at the executive level. The
implementation of organization-wide initiatives in the Improve stage may
05_Pyzdek_Ch05_p061-102.indd 70 11/9/12 5:04 PM