Page 73 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 73
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 58
58 back scatter • bail
backup facility In an electrical or communications
system, a facility that is intended for use when
the primary, or main, facility is not operational.
back voltage 1. Voltage induced in an inductor by
the flow of current through the inductor, so called
because its polarity is opposite to that of the ap-
plied voltage. Also called counter emf. 2. A voltage
used to obtain bucking action (e.g., the voltage
used to zero the meter in an electronic voltmeter
circuit). 3. Reverse voltage applied to a semicon-
ductor junction.
backwall In a pot core, the plate or disk that con-
nects the sleeve and center post to close the mag-
netic circuit.
backward diode A semiconductor diode manufac-
tured in such a way that its high-current flow oc-
curs when the junction is reverse biased. Such a
diode is also a negative-resistance device.
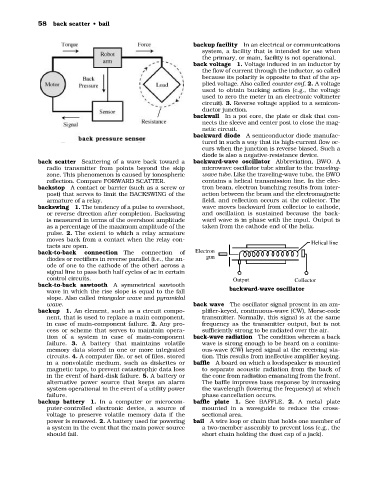
back scatter Scattering of a wave back toward a backward-wave oscillator Abbreviation, BWO. A
radio transmitter from points beyond the skip microwave oscillator tube similar to the traveling-
zone. This phenomenon is caused by ionospheric wave tube. Like the traveling-wave tube, the BWO
reflection. Compare FORWARD SCATTER. contains a helical transmission line. In the elec-
backstop A contact or barrier (such as a screw or tron beam, electron bunching results from inter-
post) that serves to limit the BACKSWING of the action between the beam and the electromagnetic
armature of a relay. field, and reflection occurs at the collector. The
backswing 1. The tendency of a pulse to overshoot, wave moves backward from collector to cathode,
or reverse direction after completion. Backswing and oscillation is sustained because the back-
is measured in terms of the overshoot amplitude ward wave is in phase with the input. Output is
as a percentage of the maximum amplitude of the taken from the cathode end of the helix.
pulse. 2. The extent to which a relay armature
moves back from a contact when the relay con- Helical line
tacts are open.
back-to-back connection The connection of Electron
diodes or rectifiers in reverse parallel (i.e., the an- gun
ode of one to the cathode of the other) across a
signal line to pass both half cycles of ac in certain
control circuits. Output Collector
back-to-back sawtooth A symmetrical sawtooth
wave in which the rise slope is equal to the fall backward-wave oscillator
slope. Also called triangular wave and pyramidal
wave. back wave The oscillator signal present in an am-
backup 1. An element, such as a circuit compo- plifier-keyed, continuous-wave (CW), Morse-code
nent, that is used to replace a main component, transmitter. Normally, this signal is at the same
in case of main-component failure. 2. Any pro- frequency as the transmitter output, but is not
cess or scheme that serves to maintain opera- sufficiently strong to be radiated over the air.
tion of a system in case of main-component back-wave radiation The condition wherein a back
failure. 3. A battery that maintains volatile wave is strong enough to be heard on a continu-
memory data stored in one or more integrated ous-wave (CW) keyed signal at the receiving sta-
circuits. 4. A computer file, or set of files, stored tion. This results from ineffective amplifier keying.
in a nonvolatile medium, such as diskettes or baffle A board on which a loudspeaker is mounted
magnetic tape, to prevent catastrophic data loss to separate acoustic radiation from the back of
in the event of hard-disk failure. 5. A battery or the cone from radiation emanating from the front.
alternative power source that keeps an alarm The baffle improves bass response by increasing
system operational in the event of a utility power the wavelength (lowering the frequency) at which
failure. phase cancellation occurs.
backup battery 1. In a computer or microcom- baffle plate 1. See BAFFLE. 2. A metal plate
puter-controlled electronic device, a source of mounted in a waveguide to reduce the cross-
voltage to preserve volatile memory data if the sectional area.
power is removed. 2. A battery used for powering bail A wire loop or chain that holds one member of
a system in the event that the main power source a two-member assembly to prevent loss (e.g., the
should fail. short chain holding the dust cap of a jack).