Page 79 - The Illustrated Dictionary of Electronics
P. 79
5059F-pB_56-92 4/9/01 4:45 PM Page 64
64 baseband frequency response • BASIC
transmission, it is about 10 Hz to 20 kHz or 30
kHz; for fast-scan television, it consists of fre-
quencies up to several megahertz. This range is
determined by bandpass and/or lowpass filters
in the AF or composite video section of the trans-
mitter.
base bias The steady dc voltage applied to the base
electrode of a transistor to determine the operat-
ing point along the transistor characteristic
curve.
base-bulk resistance The resistance of the semi-
conductor material in the base layer of a bipolar
transistor.
base-charging capacitance In the common-
emitter connection of a bipolar transistor, the in-
ternal capacitance of the base-emitter junction.
base current Symbol, I B. Current flowing through Base
the base electrode of a bipolar transistor. Also see line
AC BASE CURRENT and DC BASE CURRENT.
base electrode See BASE, 1. Also called base ele-
ment.
base element 1. Base electrode. 2. One of the ba-
sic metals, such as iron or tin, that are not gen-
erally considered precious (as opposed to base line
NOBLE).
base-e logarithm See NAPIERIAN LOGARITHM.
base film The plastic substrate of a magnetic used to provide support for the device and to al-
recording tape. low a physical connection between the socket ter-
base frequency 1. The frequency of the principal, minal, into which it fits, and one of the internal
or strongest, component in a complex signal or electrodes of the device.
waveform; also called basic frequency. 2. The fre- base plate The chassis plate upon which compo-
quency of operation of a base-station transmitter nents are mounted before wiring.
when the receiver is tuned to a second channel. base potential See BASE VOLTAGE.
base-input circuit A common-collector circuit, base region See BASE, 1.
common-emitter circuit, or emitter follower. base resistance Symbol, R B. Resistance associated
base insulator A stout dielectric insulator, used to with the base electrode of a bipolar transistor.
support a heavy conducting element and keep the Also see AC BASE RESISTANCE and DC BASE
conductor isolated from other possible conduc- RESISTANCE.
tors or conductive paths. base resistor The external resistor connected to
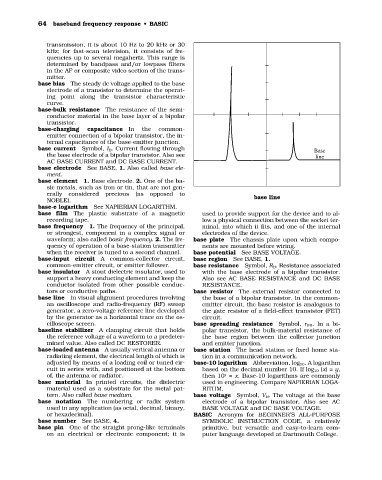
base line In visual alignment procedures involving the base of a bipolar transistor. In the common-
an oscilloscope and radio-frequency (RF) sweep emitter circuit, the base resistor is analogous to
generator, a zero-voltage reference line developed the gate resistor of a field-effect transistor (FET)
by the generator as a horizontal trace on the os- circuit.
cilloscope screen. base spreading resistance Symbol, r BB. In a bi-
baseline stabilizer A clamping circuit that holds polar transistor, the bulk-material resistance of
the reference voltage of a waveform to a predeter- the base region between the collector junction
mined value. Also called DC RESTORER. and emitter junction.
base-loaded antenna A usually vertical antenna or base station The head station or fixed home sta-
radiating element, the electrical length of which is tion in a communication network.
adjusted by means of a loading coil or tuned cir- base-10 logarithm Abbreviation, log 10. A logarithm
cuit in series with, and positioned at the bottom based on the decimal number 10. If log 10 (x) = y,
y
of, the antenna or radiator. then 10 = x. Base-10 logarithms are commonly
base material In printed circuits, the dielectric used in engineering. Compare NAPIERIAN LOGA-
material used as a substrate for the metal pat- RITHM.
tern. Also called base medium. base voltage Symbol, V B. The voltage at the base
base notation The numbering or radix system electrode of a bipolar transistor. Also see AC
used in any application (as octal, decimal, binary, BASE VOLTAGE and DC BASE VOLTAGE.
or hexadecimal). BASIC Acronym for BEGINNER’S ALL-PURPOSE
base number See BASE, 4. SYMBOLIC INSTRUCTION CODE, a relatively
base pin One of the straight prong-like terminals primitive, but versatile and easy-to-learn com-
on an electrical or electronic component; it is puter language developed at Dartmouth College.