Page 264 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 264
239
REFLECTION OF SOUND
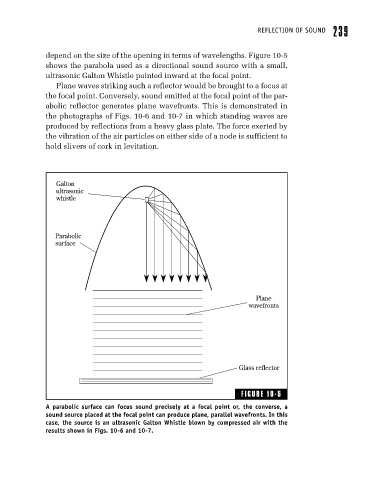
depend on the size of the opening in terms of wavelengths. Figure 10-5
shows the parabola used as a directional sound source with a small,
ultrasonic Galton Whistle pointed inward at the focal point.
Plane waves striking such a reflector would be brought to a focus at
the focal point. Conversely, sound emitted at the focal point of the par-
abolic reflector generates plane wavefronts. This is demonstrated in
the photographs of Figs. 10-6 and 10-7 in which standing waves are
produced by reflections from a heavy glass plate. The force exerted by
the vibration of the air particles on either side of a node is sufficient to
hold slivers of cork in levitation.
Galton
ultrasonic
whistle
Parabolic
surface
Plane
wavefronts
Glass reflector
FIGURE 10-5
A parabolic surface can focus sound precisely at a focal point or, the converse, a
sound source placed at the focal point can produce plane, parallel wavefronts. In this
case, the source is an ultrasonic Galton Whistle blown by compressed air with the
results shown in Figs. 10-6 and 10-7.