Page 96 - The Master Handbook Of Acoustics
P. 96
71
THE EAR AND THE PERCEPTION OF SOUND
them with the measured values of attack and decay. When this was done,
the listening jury unanimously voted that the synthetic sounds did not
sound like piano sounds but more like organ tones. Further study
revealed the long-known fact that piano strings are very stiff and have
properties of both solid rods and stretched strings. The effect of this is
that piano partials are nonharmonic! By correcting the frequencies of
what were assumed to be harmonics in integral multiples, the jury could
not distinguish between the synthetic piano sounds and the real thing.
The critical faculty of the ears of the jury in comparing sound qualities
provided the key.
An Auditory Analyzer: An Experiment
Knowledge of the ear’s filterlike critical bands leads to the tantalizing
idea of analyzing continuous noises such as traffic noises, underwater
background noises, etc., by using the ear instead of heavy and expen-
sive sound-analyzing gear. This must have occurred to Harvey
Fletcher, who first proposed the idea of critical bands, and to many
investigators in this field who have dealt with critical bands through
the years.
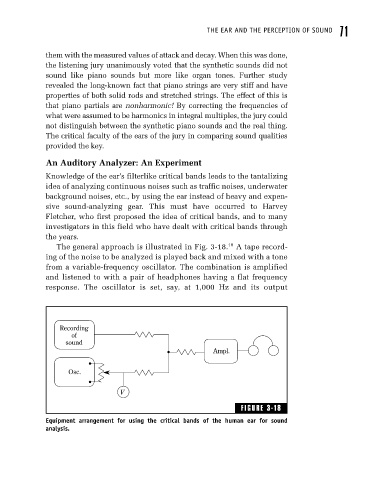
The general approach is illustrated in Fig. 3-18. 18 A tape record-
ing of the noise to be analyzed is played back and mixed with a tone
from a variable-frequency oscillator. The combination is amplified
and listened to with a pair of headphones having a flat frequency
response. The oscillator is set, say, at 1,000 Hz and its output
Recording
of
sound
Ampl.
Osc.
V
FIGURE 3-18
Equipment arrangement for using the critical bands of the human ear for sound
analysis.