Page 37 - The Memory Program How to Prevent Memory Loss and Enhance Memory Power
P. 37
Page 26
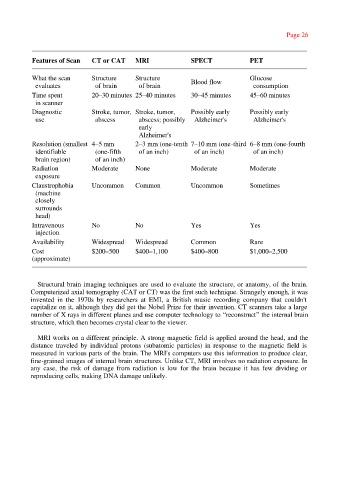
Features of Scan CT or CAT MRI SPECT PET
What the scan Structure Structure Glucose
evaluates of brain of brain Blood flow consumption
Time spent 20–30 minutes 25–40 minutes 30–45 minutes 45–60 minutes
in scanner
Diagnostic Stroke, tumor, Stroke, tumor, Possibly early Possibly early
use abscess abscess; possibly Alzheimer's Alzheimer's
early
Alzheimer's
Resolution (smallest 4–5 mm 2–3 mm (one-tenth 7–10 mm (one-third 6–8 mm (one-fourth
identifiable (one-fifth of an inch) of an inch) of an inch)
brain region) of an inch)
Radiation Moderate None Moderate Moderate
exposure
Claustrophobia Uncommon Common Uncommon Sometimes
(machine
closely
surrounds
head)
Intravenous No No Yes Yes
injection
Availability Widespread Widespread Common Rare
Cost $200–500 $400–1,100 $400–800 $1,000–2,500
(approximate)
Structural brain imaging techniques are used to evaluate the structure, or anatomy, of the brain.
Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT) was the first such technique. Strangely enough, it was
invented in the 1970s by researchers at EMI, a British music recording company that couldn't
capitalize on it, although they did get the Nobel Prize for their invention. CT scanners take a large
number of X rays in different planes and use computer technology to “reconstruct” the internal brain
structure, which then becomes crystal clear to the viewer.
MRI works on a different principle. A strong magnetic field is applied around the head, and the
distance traveled by individual protons (subatomic particles) in response to the magnetic field is
measured in various parts of the brain. The MRI's computers use this information to produce clear,
fine-grained images of internal brain structures. Unlike CT, MRI involves no radiation exposure. In
any case, the risk of damage from radiation is low for the brain because it has few dividing or
reproducing cells, making DNA damage unlikely.