Page 130 - The Petroleum System From Source to Trap
P. 130
124 Morse
A
Simple
Dune PREVAILING
WINDS
/ 8
Interdune
Simple
Dune
Interdune
r Simple
1 - 40m Dune
j_
0- 1 50m
1 00- 7 00m
" D OWNWIND" DEPOSITIONAL
ENVIRONMENTS
0- 1 00m
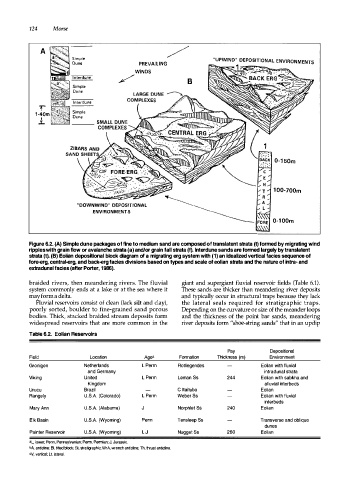
Figure 6.2. (A) Simple dune packages of fine to medium sand are composed of translatent strata (t) formed by migrating wind
ripples with grain flow or avalanche strata (a) and/or grain fall strata (f). Interdune sands are formed largely by translatent
strata (t). (B) Eolian depositional block diagram of a migrating erg system with (1) an idealized vertical facies sequence of
fore-erg, central-erg, and back-erg facies divisions based on types and scale of eolian strata and the nature of intra- and
extradunal facies (after Porter, 1986).
braided rivers, then meandering rivers. The fluvial giant and supergiant fluvial reservoir fields (Table 6.1).
system commonly ends at a lake or at the sea where it These sands are thicker than meandering river deposits
may form a delta. and typically occur in structural traps because they lack
Fluvial reservoirs consist of clean (lack silt and clay), the lateral seals required for stratigraphic traps.
poorly sorted, boulder to fine-grained sand porous Depending on the curvature or size of the meander loops
bodies. Thick, stacked braided stream deposits form and the thickness of the point bar sands, meandering
widespread reservoirs that are more common in the river deposits form "shoe-string sands" that in an updip
Table 6.2. Eolian Reservoirs
Pay Depositional
Field Location Agea Formation Thickness (m) Environment
Gronigen Netherlands L Perm Rotliegendes Eolian with fluvial
and Germany intradunal strata
Viking United L Perm Leman Ss 244 Eolian with sabkha and
Kingdom alluvial interbeds
Urucu Brazil C ltaituba Eolian
Rangely U.S.A. (Colorado) L Perm Weber Ss Eolian with fluvial
interbeds
Mary Ann U.S.A. (Alabama) J Norphlet Ss 240 Eolian
Elk Basin U.S.A. (Wyoming) Penn Tensleep Ss Transverse and oblique
dunes
Painter Reservoir U.S.A. (Wyoming) L J Nugget Ss 260 Eolian
aL, lower, Penn, Pennsylvanian; Perm, Permian; J, Jurassic.
bA, antidine: 81. Med block; St. stratigraphic; WrA. wrench antidine; Th, thrust anticline.
cv, vertical; Lt, lateral.