Page 15 - Welding of Aluminium and its Alloys
P. 15
Introduction to the welding of aluminium 7
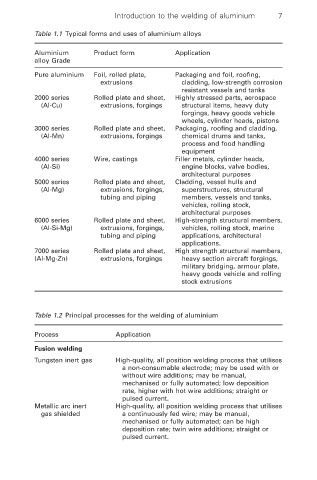
Table 1.1 Typical forms and uses of aluminium alloys
Aluminium Product form Application
alloy Grade
Pure aluminium Foil, rolled plate, Packaging and foil, roofing,
extrusions cladding, low-strength corrosion
resistant vessels and tanks
2000 series Rolled plate and sheet, Highly stressed parts, aerospace
(Al-Cu) extrusions, forgings structural items, heavy duty
forgings, heavy goods vehicle
wheels, cylinder heads, pistons
3000 series Rolled plate and sheet, Packaging, roofing and cladding,
(Al-Mn) extrusions, forgings chemical drums and tanks,
process and food handling
equipment
4000 series Wire, castings Filler metals, cylinder heads,
(Al-Si) engine blocks, valve bodies,
architectural purposes
5000 series Rolled plate and sheet, Cladding, vessel hulls and
(Al-Mg) extrusions, forgings, superstructures, structural
tubing and piping members, vessels and tanks,
vehicles, rolling stock,
architectural purposes
6000 series Rolled plate and sheet, High-strength structural members,
(Al-Si-Mg) extrusions, forgings, vehicles, rolling stock, marine
tubing and piping applications, architectural
applications.
7000 series Rolled plate and sheet, High strength structural members,
(Al-Mg-Zn) extrusions, forgings heavy section aircraft forgings,
military bridging, armour plate,
heavy goods vehicle and rolling
stock extrusions
Table 1.2 Principal processes for the welding of aluminium
Process Application
Fusion welding
Tungsten inert gas High-quality, all position welding process that utilises
a non-consumable electrode; may be used with or
without wire additions; may be manual,
mechanised or fully automated; low deposition
rate, higher with hot wire additions; straight or
pulsed current.
Metallic arc inert High-quality, all position welding process that utilises
gas shielded a continuously fed wire; may be manual,
mechanised or fully automated; can be high
deposition rate; twin wire additions; straight or
pulsed current.