Page 46 - The engineering of chemical reactions
P. 46
30 Reaction Rates, the Batch Reactor, and the Real World
Reaction rate expressions are always empirical, which means that we use whatever
expression gives an accurate enough description of the problem at hand. No reactions are as
simple as these expressions predict if we need them to be correct to many decimal places.
Further, all reaction systems in fact involve multiple reactions, and there is no such thing
as a truly irreversible reaction if we could measure all species to sufficient accuracy. If we
need a product with impurities at the parts per billion (ppb) level, then all reactions are in
fact reversible and involve many reactions.
Chemical engineers get paid to make whatever approximations are reasonable to find
answers at the level of sophisticatiqn required for the problem at hand. If this were easy,
our salaries would be lower.
RATE COEFFICIENTS
We next consider the ks in the above expressions. We will generally call these the rate
coejficients (the coefficient of the concentration dependences in r). They are sometimes
called rate constants; they are independent of concentrations, but rate coefficients are almost
always strong functions of temperature.
It is found empirically that these coefficients frequently depend on temperature as
1 k(T) = kOemEIRT 1
where E is called the activation energy for the reaction and k, is called (unimaginatively)
the pre-exponential factor.
This relation is credited to Svante Arrhenius and is called the Arrhenius temperature
dependence. Arrhenius was mainly concerned with thermodynamics and chemical equilib-
rium. Some time later Michael Polanyi and Eugene Wigner showed that simple molecular
arguments lead to this temperature dependence, and this form of the rate is frequently called
the Polanyi-Wigner relation. They described chemical reactions as the process of crossing
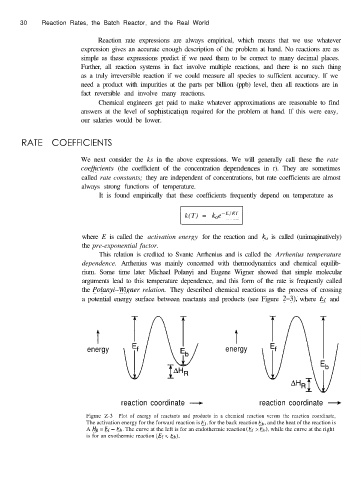
a potential energy surface between reactants and products (see Figure 2-3), where Ef and
t t
energy energy
reaction coordinate --+ reaction coordinate -
Figure Z-3 Plot of energy of reactants and products in a chemical reaction versus the reaction coordinate,
The activation energy for the forward reaction is Ef, for the back reaction Eb. and the heat of the reaction is
A HR = & - &. The curve at the left is for an endothermic reaction (Ef > &). while the curve at the right
is for an exothermic reaction (Ef < &).