Page 59 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 59
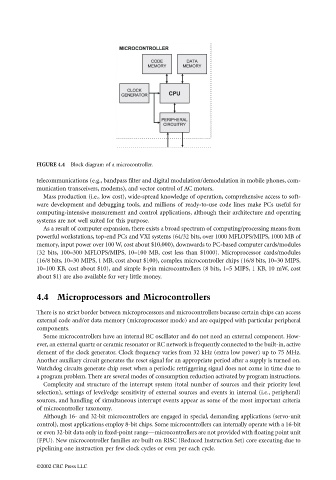
FIGURE 4.4 Block diagram of a microcontroller.
telecommunications (e.g., bandpass filter and digital modulation/demodulation in mobile phones, com-
munication transceivers, modems), and vector control of AC motors.
Mass production (i.e., low cost), wide-spread knowledge of operation, comprehensive access to soft-
ware development and debugging tools, and millions of ready-to-use code lines make PCs useful for
computing-intensive measurement and control applications, although their architecture and operating
systems are not well suited for this purpose.
As a result of computer expansion, there exists a broad spectrum of computing/processing means from
powerful workstations, top-end PCs and VXI systems (64/32 bits, over 1000 MFLOPS/MIPS, 1000 MB of
memory, input power over 100 W, cost about $10,000), downwards to PC-based computer cards/modules
(32 bits, 100–300 MFLOPS/MIPS, 10–100 MB, cost less than $1000). Microprocessor cards/modules
(16/8 bits, 10–30 MIPS, 1 MB, cost about $100), complex microcontroller chips (16/8 bits, 10–30 MIPS,
10–100 KB, cost about $10), and simple 8-pin microcontrollers (8 bits, 1–5 MIPS, 1 KB, 10 mW, cost
about $1) are also available for very little money.
4.4 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
There is no strict border between microprocessors and microcontrollers because certain chips can access
external code and/or data memory (microprocessor mode) and are equipped with particular peripheral
components.
Some microcontrollers have an internal RC oscillator and do not need an external component. How-
ever, an external quartz or ceramic resonator or RC network is frequently connected to the built-in, active
element of the clock generator. Clock frequency varies from 32 kHz (extra low power) up to 75 MHz.
Another auxiliary circuit generates the reset signal for an appropriate period after a supply is turned on.
Watchdog circuits generate chip reset when a periodic retriggering signal does not come in time due to
a program problem. There are several modes of consumption reduction activated by program instructions.
Complexity and structure of the interrupt system (total number of sources and their priority level
selection), settings of level/edge sensitivity of external sources and events in internal (i.e., peripheral)
sources, and handling of simultaneous interrupt events appear as some of the most important criteria
of microcontroller taxonomy.
Although 16- and 32-bit microcontrollers are engaged in special, demanding applications (servo-unit
control), most applications employ 8-bit chips. Some microcontrollers can internally operate with a 16-bit
or even 32-bit data only in fixed-point range—microcontrollers are not provided with floating point unit
(FPU). New microcontroller families are built on RISC (Reduced Instruction Set) core executing due to
pipelining one instruction per few clock cycles or even per each cycle.
©2002 CRC Press LLC