Page 668 - Bird R.B. Transport phenomena
P. 668
648 Chapter 20 Concentration Distributions with More Than One Independent Variable
PROBLEMS 20A.1. Measurement of diffusivity by unsteady-state evaporation. Use the following data to
determine the diffusivity of ethyl propionate (species A) into a mixture of 20 mole% air and
80 mole% hydrogen (this mixture being treated as a pure gas B). 1
3
Increase in vapor volume (cm ) Vt(s l 2 )
0.01 15.5
0.11 19.4
0.22 23.4
0.31 26.9
0.41 30.5
0.50 34.0
0.60 37.5
0.70 41.5
These data were obtained 1 by using a glass tube 200 cm long, with an inside diameter 1.043
cm; the temperature was 27.9°C and the pressure 761.2 mm Hg. The vapor pressure of ethyl
propionate at this temperature is 41.5 mm Hg. Note that t is the actual time from the start of
the evaporation, whereas the volume increase is measured from t ~ 240 s.
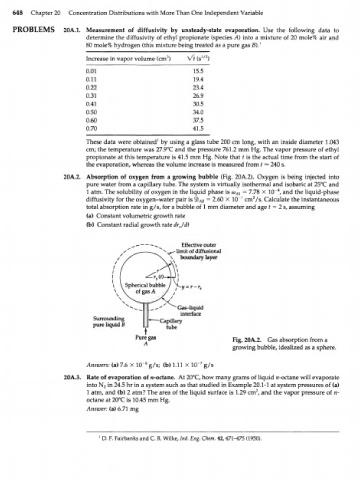
20A.2. Absorption of oxygen from a growing bubble (Fig. 20A.2). Oxygen is being injected into
pure water from a capillary tube. The system is virtually isothermal and isobaric at 25°C and
4
1 atm. The solubility of oxygen in the liquid phase is <о А0 = 7.78 X 10" , and the liquid-phase
2
diffusivity for the oxygen-water pair is %b AB = 2.60 X 10" : cm /s. Calculate the instantaneous
total absorption rate in g/s, for a bubble of 1 mm diameter and age t = 2 s, assuming
(a) Constant volumetric growth rate
(b) Constant radial growth rate drjdt
Effective outer
limit of diffusional
boundary layer
Gas-liquid
interface
Surrounding
pure liquid В
Fig. 20A.2. Gas absorption from a
growing bubble, idealized as a sphere.
Answers: (a) 7.6 X 10~ g/s; (b) 1.11 X 10' 7 g/s
8
20A.3. Rate of evaporation of и-octane. At 20°C, how many grams of liquid и-octane will evaporate
into N in 24.5 hr in a system such as that studied in Example 20.1-1 at system pressures of (a)
2
2
1 atm, and (b) 2 atm? The area of the liquid surface is 1.29 cm , and the vapor pressure of n-
octane at 20°C is 10.45 mm Hg.
Answer: (a) 6.71 mg
D. F. Fairbanks and С R. Wilke, Ind. Eng. Chem. 42, 471^75 (1950).
1