Page 174 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 174
140 Cha pte r F o u r
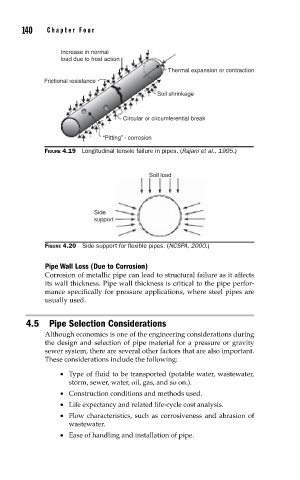
Increase in normal
load due to frost action
Thermal expansion or contraction
Frictional resistance
Soil shrinkage
Circular or circumferential break
“Pitting” - corrosion
FIGURE 4.19 Longitudinal tensile failure in pipes. (Rajani et al., 1995.)
Soil load
Side
support
FIGURE 4.20 Side support for fl exible pipes. (NCSPA, 2000.)
Pipe Wall Loss (Due to Corrosion)
Corrosion of metallic pipe can lead to structural failure as it affects
its wall thickness. Pipe wall thickness is critical to the pipe perfor-
mance specifically for pressure applications, where steel pipes are
usually used.
4.5 Pipe Selection Considerations
Although economics is one of the engineering considerations during
the design and selection of pipe material for a pressure or gravity
sewer system, there are several other factors that are also important.
These considerations include the following:
• Type of fluid to be transported (potable water, wastewater,
storm, sewer, water, oil, gas, and so on.).
• Construction conditions and methods used.
• Life expectancy and related life-cycle cost analysis.
• Flow characteristics, such as corrosiveness and abrasion of
wastewater.
• Ease of handling and installation of pipe.