Page 200 - Trenchless Technology Piping Installation and Inspection
P. 200
164 Cha pte r F o u r
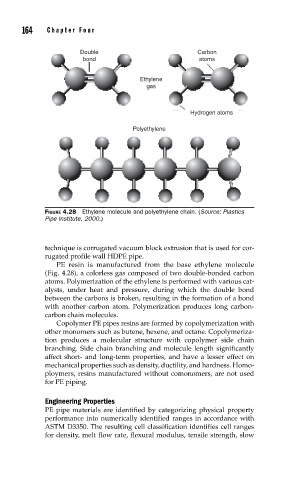
Double Carbon
bond atoms
Ethylene
gas
Hydrogen atoms
Polyethylene
FIGURE 4.28 Ethylene molecule and polyethylene chain. (Source: Plastics
Pipe Institute, 2000.)
technique is corrugated vacuum block extrusion that is used for cor-
rugated profile wall HDPE pipe.
PE resin is manufactured from the base ethylene molecule
(Fig. 4.28), a colorless gas composed of two double-bonded carbon
atoms. Polymerization of the ethylene is performed with various cat-
alysts, under heat and pressure, during which the double bond
between the carbons is broken, resulting in the formation of a bond
with another carbon atom. Polymerization produces long carbon-
carbon chain molecules.
Copolymer PE pipes resins are formed by copolymerization with
other monomers such as butene, hexene, and octane. Copolymeriza-
tion produces a molecular structure with copolymer side chain
branching. Side chain branching and molecule length significantly
affect short- and long-term properties, and have a lesser effect on
mechanical properties such as density, ductility, and hardness. Homo-
ploymers, resins manufactured without comonomers, are not used
for PE piping.
Engineering Properties
PE pipe materials are identified by categorizing physical property
performance into numerically identified ranges in accordance with
ASTM D3350. The resulting cell classification identifies cell ranges
for density, melt flow rate, flexural modulus, tensile strength, slow