Page 53 - Tunable Lasers Handbook
P. 53
34 R. C. Sze and D. G. Harris
originate by field emission from a cathode (frequently carbon felt), which has
been negatively pulsed with respect to the anode, generally maintained at
ground. The vacuum diode (generally operating at 10-5 to 10-7 Torr) is separated
from the high-pressure laser gases by a thin foil. The emitted electrons pass
through the foil, though losing some energy, and enter the lasing media, creating
ions. Although large and expensive. these devices are easily scaled to meter
dimensions and allow long-pulse (1 psec or greater) pumping. They are therefore
generally used as amplifiers rather than oscillators.
Preionized avalanche discharges have been utilized to produce a uniform
plasma. The low-energy electrons in the plasma acquire sufficient energy to
excite the rare gas atoms to a metastable state, thus allowing the reaction kinetics
to proceed along the neutral reaction channel. The relative ease and low cost of
this approach has led to the rapid development of high-average-power lasers.
Discharge excimer lasers are discussed in Section 4.
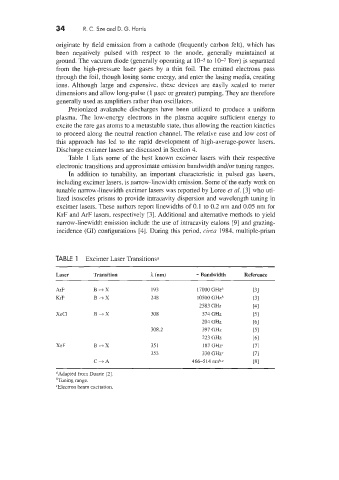
Table 1 lists some of the best known excimer lasers with their respective
electronic transitions and approximate emission bandwidth andlor tuning ranges.
In addition to tunability, an important characteristic in pulsed gas lasers.
including excimer lasers, is narrow-linewidth emission. Some of the early work on
tunable narrow-linewidth excimer lasers was reported by Loree et al. [3] who uti-
lized isosceles prisms to provide intracavity dispersion and wavelength tuning in
excimer lasers. These authors report linewidths of 0.1 to 0.2 nm and 0.05 nm for
KrF and ArF lasers, respectively [3]. Additional and alternative methods to yield
narrow-linewidth emission include the use of intracavity etalons [9] and grazing-
incidence (GI) configurations [4]. During this period. circa 1981. multiple-prism
TABLE 1 Excimer Laser Transitions0
Laser Transition h (nm) - Bandwidth Reference
.AIF B+X 193 17000 GHzh
KrF B+X 218 10500 GHzh
2583 GHz
XZCl B+X 308 374 GHz
201 GHz
308.2 397 GHz
223 GHz
XeF B-1X 35 1 187 GHzc
353 330 GHzr
C+A 466-514 nmhc
OAdapted from Duarte [2].
hTuning range.
‘Elecuon beam excitation.