Page 37 - Understanding Automotive Electronics
P. 37
2735 | CH 1 Page 24 Tuesday, March 10, 1998 10:52 AM
1 AUTOMOTIVE FUNDAMENTALS
Electronic control of braking benefits safety by improving stopping
performance in poor or marginal braking conditions. Chapter 8 explains the
operation of the so-called antilock braking system (ABS).
STEERING SYSTEM
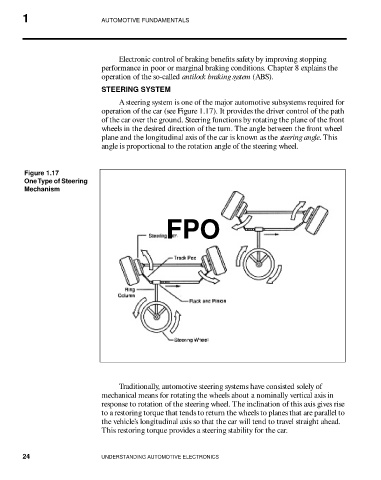
A steering system is one of the major automotive subsystems required for
operation of the car (see Figure 1.17). It provides the driver control of the path
of the car over the ground. Steering functions by rotating the plane of the front
wheels in the desired direction of the turn. The angle between the front wheel
plane and the longitudinal axis of the car is known as the steering angle. This
angle is proportional to the rotation angle of the steering wheel.
Figure 1.17
One Type of Steering
Mechanism
FPO
Traditionally, automotive steering systems have consisted solely of
mechanical means for rotating the wheels about a nominally vertical axis in
response to rotation of the steering wheel. The inclination of this axis gives rise
to a restoring torque that tends to return the wheels to planes that are parallel to
the vehicle’s longitudinal axis so that the car will tend to travel straight ahead.
This restoring torque provides a steering stability for the car.
24 UNDERSTANDING AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS